A moving DNA replication factory in Caulobacter crescentus
- PMID: 11532959
- PMCID: PMC125615
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4952
A moving DNA replication factory in Caulobacter crescentus
Abstract
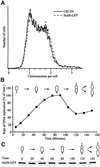
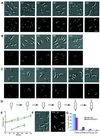
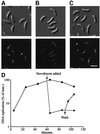
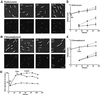
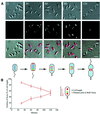
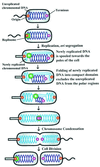
The in vivo intracellular location of components of the Caulobacter replication apparatus was visualized during the cell cycle. Replisome assembly occurs at the chromosomal origin located at the stalked cell pole, coincident with the initiation of DNA replication. The replisome gradually moves to midcell as DNA replication proceeds and disassembles upon completion of DNA replication. Although the newly replicated origin regions of the chromosome are rapidly moved to opposite cell poles by an active process, the replisome appears to be an untethered replication factory that is passively displaced towards the center of the cell by the newly replicated DNA. These results are consistent with a model in which unreplicated DNA is pulled into the replication factory and newly replicated DNA is bidirectionally extruded from the complex, perhaps contributing to chromosome segregation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caulobacter requires a dedicated mechanism to initiate chromosome segregation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 7;105(40):15435-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807448105. Epub 2008 Sep 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18824683 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination between chromosome replication, segregation, and cell division in Caulobacter crescentus.J Bacteriol. 2006 Mar;188(6):2244-53. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.6.2244-2253.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16513754 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle regulation in Caulobacter: location, location, location.J Cell Sci. 2007 Oct 15;120(Pt 20):3501-7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.005967. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17928306 Review.
-
A polymeric protein anchors the chromosomal origin/ParB complex at a bacterial cell pole.Cell. 2008 Sep 19;134(6):945-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.015. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18805088 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of chromosomal replication in Caulobacter crescentus.Plasmid. 2012 Mar;67(2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2011.12.007. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Plasmid. 2012. PMID: 22227374 Review.
Cited by
-
Choreography of the Mycobacterium replication machinery during the cell cycle.mBio. 2015 Feb 17;6(1):e02125-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02125-14. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25691599 Free PMC article.
-
The Origin of Chromosomal Replication Is Asymmetrically Positioned on the Mycobacterial Nucleoid, and the Timing of Its Firing Depends on HupB.J Bacteriol. 2018 Apr 24;200(10):e00044-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00044-18. Print 2018 May 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29531181 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial chromosome organization and segregation.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015;31:171-99. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125211. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26566111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex regulatory pathways coordinate cell-cycle progression and development in Caulobacter crescentus.Adv Microb Physiol. 2009;54:1-101. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2911(08)00001-5. Adv Microb Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18929067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromosome organization shapes replisome dynamics in Caulobacter crescentus.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 24;15(1):3460. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47849-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38658616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cook P.R. (1999) The organization of replication and transcription. Science, 284, 1790–1795. - PubMed
-
- Davey M.J. and O’Donnell,M. (2000) Mechanisms of DNA replication. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 4, 581–586. - PubMed
-
- Dingman C.W. (1974) Bidirectional chromosome replication: some topological considerations. J. Theor. Biol., 43, 187–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

