Optimising testing for phospholipid antibodies
- PMID: 11533076
- PMCID: PMC1731506
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.54.9.693
Optimising testing for phospholipid antibodies
Abstract
Aim: To compare anticardiolipin (ACL) and anti-beta2 glycoprotein 1 (beta2gp1) enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) in the diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and to incorporate these results into a meta-analysis of published data.
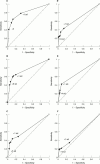
Method: Three representative commercial ACL ELISAs and an in house beta2gp1 assay were optimised and then assessed on 124 sera from normal donors, patients with infection, or patients with APS. A Medline search was screened for papers meeting defined criteria to conduct a meta-analysis. The performance of the assays used in this study was included.
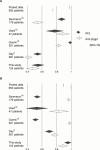
Results: A non-quantitative ACL assay performed at least as well as the anti-beta2gp1 assay in the diagnosis of APS. Meta-analysis confirmed that neither assay is perfect, although the anti-beta2gp1 assay had a higher specificity and lower sensitivity than the ACL assay.
Conclusions: The pooled data suggest that the ACL assay is used to investigate thrombosis without overt underlying pathology and that the improved specificity of the anti-beta2gp1 assay is exploited where infection, connective tissue disease, or atheroma are present.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
