Open probability of homomeric murine 5-HT3A serotonin receptors depends on subunit occupancy
- PMID: 11533135
- PMCID: PMC2278792
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00427.x
Open probability of homomeric murine 5-HT3A serotonin receptors depends on subunit occupancy
Abstract
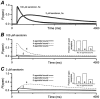
1. The time course of macroscopic current responses of homomeric murine serotonin 5-HT3A receptors was studied in whole cells and excised membrane patches under voltage clamp in response to rapid application of serotonin. 2. Serotonin activated whole cell currents with an EC(50) value for the peak response of 2 microM and a Hill slope of 3.0 (n = 12), suggesting that the binding of at least three agonist molecules is required to open the channel. 3. Homomeric 5-HT3A receptors in excised membrane patches had a slow activation time course (mean +/- S.E.M. 10-90 % rise time 12.5 +/- 1.6 ms; n = 9 patches) for 100 microM serotonin. The apparent activation rate was estimated by fitting an exponential function to the rising phase of responses to supramaximal serotonin to be 136 s(-1). 4. The 5-HT3A receptor response to 100 microM serotonin in outside-out patches (n = 19) and whole cells (n = 41) desensitized with a variable rate that accelerated throughout the experiment. The time course for desensitization was described by two exponential components (for patches tau(slow) 1006 +/- 139 ms, amplitude 31 %; tau(fast) 176 +/- 25 ms, amplitude 69 %). 5. Deactivation of the response following serotonin removal from excised membrane patches (n = 8) and whole cells (n = 29) was described by a dual exponential time course with time constants similar to those for desensitization (for patches tau(slow) 838 +/- 217 ms, 55 % amplitude; tau(fast) 213 +/- 44 ms, 45 % amplitude). 6. In most patches (6 of 8), the deactivation time course in response to a brief 1-5 ms pulse of serotonin was similar to or slower than desensitization. This suggests that the continued presence of agonist can induce desensitization with a similar or more rapid time course than agonist unbinding. The difference between the time course for deactivation and desensitization was voltage independent over the range -100 to -40 mV in patches (n = 4) and -100 to +50 mV in whole cells (n = 4), suggesting desensitization of these receptors in the presence of serotonin does not reflect a voltage-dependent block of the channel by agonist. 7. Simultaneously fitting the macroscopic 5-HT3A receptor responses in patches to submaximal (2 microM) and maximal (100 microM) concentrations of serotonin to a variety of state models suggests that homomeric 5-HT3A receptors require the binding of three agonists to open and possess a peak open probability greater than 0.8. Our modelling also suggests that channel open probability varies with the number of serotonin molecules bound to the receptor, with a reduced open probability for fully liganded receptors. Increasing the desensitization rate constants in this model can generate desensitization that is more rapid than deactivation, as observed in a subpopulation of our patches.
Figures

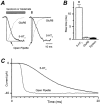

 ) current responses are shown. C, averaged amplitude ratios (mean ±
) current responses are shown. C, averaged amplitude ratios (mean ±
 ) current responses are shown. C, averaged amplitude ratios (mean ±
) current responses are shown. C, averaged amplitude ratios (mean ±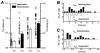



Similar articles
-
The 4'lysine in the putative channel lining domain affects desensitization but not the single-channel conductance of recombinant homomeric 5-HT3A receptors.J Physiol. 2000 Jan 15;522 Pt 2(Pt 2):187-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00187.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10639097 Free PMC article.
-
Single-channel properties of native and cloned rat vanilloid receptors.J Physiol. 2002 Nov 15;545(1):107-17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.016352. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12433953 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular actions of propofol on human 5-HT3A receptors: enhancement as well as inhibition by closely related phenol derivatives.Anesth Analg. 2008 Mar;106(3):846-57, table of contents. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e318162ca7c. Anesth Analg. 2008. PMID: 18292429
-
Control of rat GluR6 glutamate receptor open probability by protein kinase A and calcineurin.J Physiol. 1997 Sep 15;503 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):513-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.513bg.x. J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9379408 Free PMC article.
-
A new wave of serotonin receptors.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Jun;3(3):310-5. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90122-f. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993. PMID: 8369625 Review.
Cited by
-
Tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptor currents in NCB-20 cells.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;22(5):585-595. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.5.585. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30181705 Free PMC article.
-
Subunit-dependent modulation of kainate receptors by extracellular protons and polyamines.J Neurosci. 2003 Feb 15;23(4):1179-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-04-01179.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12598606 Free PMC article.
-
Subunit-specific mechanisms and proton sensitivity of NMDA receptor channel block.J Physiol. 2007 May 15;581(Pt 1):107-28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124958. Epub 2007 Feb 15. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17303642 Free PMC article.
-
Number and locations of agonist binding sites required to activate homomeric Cys-loop receptors.J Neurosci. 2009 May 6;29(18):6022-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0627-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19420269 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT3 receptor antagonism a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of depression and other disorders.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(9):1545-1559. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666201015155816. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33059577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aapro MS. Controlling emesis related to cancer therapy. European Journal of Cancer. 1991;27:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Barann M, Gothert M, Binisch H, Dybek A, Urban BW. 5-HT3 receptors in outside-out patches of N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells: basic properties and effects of pentobarbital. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:655–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

