Impact of the renin-angiotensin system on cerebral perfusion following subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat
- PMID: 11533142
- PMCID: PMC2278788
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00533.x
Impact of the renin-angiotensin system on cerebral perfusion following subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat
Abstract
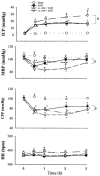
1. This study investigated the effects of blocking the AT1 angiotensin receptors with irbesartan, either peripherally or centrally, on systemic blood pressure, intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure following experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) in urethane-anaesthetized rats. Sympathetic nervous activation was determined by measuring plasma noradrenaline levels. 2. In untreated animals, SAH induced a sustained increased in intracranial pressure from 2.1 +/- 0.3 to 16 +/- 2 mmHg (3 h, P < 0.001). Cerebral perfusion pressure was reduced by 20 % (P < 0.001), this reduction being maintained for 3 h. Sympathetic activation was evident in the high level of plasma noradrenaline measured 3 h post-SAH (751 +/- 104 vs. 405 +/- 33 pg ml(-1), P < 0.05). 3. Acute peripheral pretreatment with irbesartan (3 mg kg(-1), I.V.) prevented the rise in plasma noradrenaline and further aggravated the decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure by producing transient systemic hypotension (blood pressure was 85 +/- 6 mmHg at 2 h post-SAH vs. 100 +/- 3 mmHg, P < 0.01). 4. Intracisternal pretreatment with irbesartan (0.035 mg) did not prevent the rise in plasma noradrenaline post-SAH but enhanced the rise in intracranial pressure by 75 % compared with untreated animals. 5. This study demonstrates that peripheral endogenous angiotensin II interacts with the sympathetic nervous system in order to maintain an adequate cerebral perfusion following SAH. Endogenous angiotensin II in the brain seems to exert a protective effect by counteracting the elevation in intracranial pressure that occurs following experimental SAH.
Figures


References
-
- Acikgoz B, Ozgen T, Ozdogan F, Sungur A, Tekkok IH. Angiotensin II receptor content within the subfornical organ and organum vasculosum lamina terminalis increases after experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage in rats. Acta Neurochirugica. 1996;138:460–465. - PubMed
-
- Andrews P, Papadakis N, Gavras H. Reversal of experimental acute cerebral vasospasm by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition. Stroke. 1982;13:480–483. - PubMed
-
- Astrup J, Siesjo BK, Symon L. Thresholds in cerebral ischemia - the ischemic penumbra. Stroke. 1981;12:723–725. - PubMed
-
- Barbella YR, Keil LC, Wurpel JN, Severs WB. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure during cerebroventricular infusion of angiotensin and vasopressin. Experimental Neurology. 1983;82:325–334. - PubMed
-
- Bishop V, Shade R, Haywood J. Hormonal modulation of baroreceptor reflexes. In: Persson KP, editor. Baroreceptor Reflexes. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1991. pp. 228–238.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

