Recombinant herpes simplex virus type 1 expressing murine interleukin-4 is less virulent than wild-type virus in mice
- PMID: 11533166
- PMCID: PMC114471
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9029-9036.2001
Recombinant herpes simplex virus type 1 expressing murine interleukin-4 is less virulent than wild-type virus in mice
Abstract
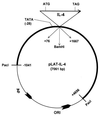
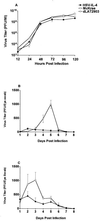
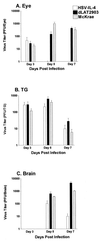
The effect of interleukin-4 (IL-4) on herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection in mice was evaluated by construction of a recombinant HSV-1 expressing the gene for murine IL-4 in place of the latency-associated transcript (LAT). The mutant virus (HSV-IL-4) expressed high levels of IL-4 in cultured cells. The replication of HSV-IL-4 in tissue culture and in trigeminal ganglia was similar to that of wild-type virus. In contrast, HSV-IL-4 appeared to replicate less well in mouse eyes and brains. Although BALB/c mice are highly susceptible to HSV-1 infection, ocular infection with HSV-IL-4 resulted in 100% survival. Furthermore, 57% of the mice survived coinfection with a mixture of HSV-IL-4 and a lethal dose of wild-type McKrae, compared with only 10% survival following infection with McKrae alone. Similar to wild-type BALB/c mice, 100% of IL-4(-/-) mice also survived HSV-IL-4 infection. T-cell depletion studies suggested that protection against HSV-IL-4 infection was mediated by a CD4(+)-T-cell response.
Figures


References
-
- Abehsira-Amar O, Gibert M, Joliy M, Theze J, Jankovic D L. IL-4 plays a dominant role in the differential development of Tho into Th1 and Th2 cells. J Immunol. 1992;148:3820–3829. - PubMed
-
- Biron C A. Cytokines in the generation of immune responses to, and resolution of, virus infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994;6:530–538. - PubMed
-
- Cheers C, Janas M, Ramsay A, Ramshaw I. Use of recombinant viruses to deliver cytokines influencing the course of experimental bacterial infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 1999;77:324–330. - PubMed
-
- Cherwinski H M, Schumacher J H, Brown K D, Mosmann T R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987;166:1229–1244. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

