Protection against woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infection by gene gun coimmunization with WHV core and interleukin-12
- PMID: 11533170
- PMCID: PMC114475
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9068-9076.2001
Protection against woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infection by gene gun coimmunization with WHV core and interleukin-12
Abstract
Woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) are closely similar with respect to genomic organization, host antiviral responses, and pathobiology of the infection. T-cell immunity against viral nucleocapsid (HBcAg or WHcAg) has been shown to play a critical role in viral clearance and protection against infection. Here we show that vaccination of healthy woodchucks by gene gun bombardment with a plasmid coding for WHcAg (pCw) stimulates proliferation of WHcAg-specific T cells but that these cells do not produce significant levels of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) upon antigen stimulation. In addition, animals vaccinated with pCw alone were not protected against WHV inoculation. In order to induce a Th1 cytokine response, another group of woodchucks was immunized with pCw together with another plasmid coding for woodchuck interleukin-12 (IL-12). These animals exhibited WHcAg-specific T-cell proliferation with high IFN-gamma production and were protected against challenge with WHV, showing no viremia or low-level transient viremia after WHV inoculation. In conclusion, gene gun immunization with WHV core generates a non-Th1 type of response which does not protect against experimental infection. However, steering the immune response to a Th1 cytokine profile by IL-12 coadministration achieves protective immunity. These data demonstrate a crucial role of Th1 responses in the control of hepadnavirus replication and suggest new approaches to inducing protection against HBV infection.
Figures
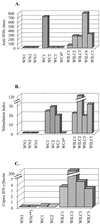
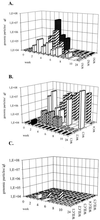
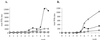
 , animals immunized with pCw plus pIL12w. Mean values at each time point are shown.
, animals immunized with pCw plus pIL12w. Mean values at each time point are shown.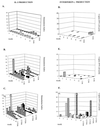
References
-
- Ausubel F A, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons; 2000.
-
- Borrow P. Mechanisms of viral clearance and persistence. J Viral Hepat. 1997;4(Suppl. 2):16–24. - PubMed
-
- Carman W F. The clinical significance of surface antigen variants of hepatitis B virus. J Viral Hepat. 1997;4(Suppl. 1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- Carman W F, Zanetti A R, Karayiannis P, Waters J, Manzillo G, Tanzi E, Zuckerman A J, Thomas H C. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet. 1990;336:325–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

