Function of Rta is essential for lytic replication of murine gammaherpesvirus 68
- PMID: 11533188
- PMCID: PMC114493
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9262-9273.2001
Function of Rta is essential for lytic replication of murine gammaherpesvirus 68
Abstract
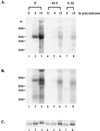
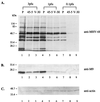
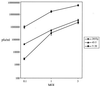
Rta, encoded primarily by open reading frame 50, is well conserved among gammaherpesviruses. It has been shown that the Rta proteins of Epstein Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV, or HHV-8), and murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68; also referred to as gamma HV68) play an important role in viral reactivation from latency. However, the role of Rta during productive de novo infection has not been characterized in gammaherpesviruses. Since there are cell lines that can support efficient productive de novo infection by MHV-68 but not EBV or KSHV, we examined whether MHV-68 Rta plays a role in initiating viral lytic replication in productively infected cells. Rta, functioning as a transcriptional activator, can activate the viral promoter of early lytic genes. The amino acid sequence alignments of the Rta homologues suggest that the organizations of their functional domains are similar, with the DNA binding and dimerization domains at the N terminus and the trans-activation domain at the C terminus. We constructed two mutants of MHV-68 Rta, Rd1 and Rd2, with deletions of 112 and 243 amino acids from the C terminus, respectively. Rd1 and Rd2 could no longer trans-activate the promoter of MHV-68 gene 57, consistent with the deletions of their trans-activation domains at the C terminus. Furthermore, Rd1 and Rd2 were able to function as dominant-negative mutants, inhibiting trans-activation of wild-type Rta. To study whether Rd1 and Rd2 blocked viral lytic replication, purified virion DNA was cotransfected with Rd1 or Rd2 into fibroblasts. Expression of viral lytic proteins was greatly suppressed, and the yield of infectious viruses was reduced up to 10(4)-fold. Stable cell lines constitutively expressing Rd2 were established and infected with MHV-68. Transcription of the immediate-early gene, rta, and the early gene, tk, of the virus was reduced in these cell lines. The presence of Rd2 also led to attenuation of viral lytic protein expression and virion production. The ability of Rta dominant-negative mutants to inhibit productive infection suggests that the trans-activation function of Rta is essential for MHV-68 lytic replication. We propose that a single viral protein, Rta, governs the initiation of MHV-68 lytic replication during both reactivation and productive de novo infection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rta of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 reactivates the complete lytic cycle from latency.J Virol. 2000 Apr;74(8):3659-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.8.3659-3667.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10729142 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
-
Lytic but not latent infection by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus requires host CSL protein, the mediator of Notch signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 8;100(14):8490-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1432843100. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12832621 Free PMC article.
-
Alternatively initiated gene 50/RTA transcripts expressed during murine and human gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(1):314-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01444-08. Epub 2008 Oct 29. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18971285 Free PMC article.
-
The Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of the gamma-herpesviridae.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:71-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089794 Review.
Cited by
-
CTCF and Sp1 interact with the Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 internal repeat elements.Virus Genes. 2012 Oct;45(2):265-73. doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0769-y. Epub 2012 Jun 16. Virus Genes. 2012. PMID: 22706977
-
Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway enhances gamma-2 herpesvirus lytic replication and facilitates reactivation from latency.J Gen Virol. 2010 Feb;91(Pt 2):463-9. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.015073-0. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Gen Virol. 2010. PMID: 19864499 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of interactions between RTA and the promoter of polyadenylated nuclear RNA in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8.J Virol. 2002 May;76(10):5000-13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.10.5000-5013.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11967316 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse gammaherpesvirus-68 infection acts as a rheostat to set the level of type I interferon signaling in primary macrophages.Virology. 2013 Aug 15;443(1):123-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.04.036. Epub 2013 May 23. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23706314 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of alternative transcripts encoding the essential murine gammaherpesvirus lytic transactivator RTA.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5474-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03110-13. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24574412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

