A cellular J-domain protein modulates polyprotein processing and cytopathogenicity of a pestivirus
- PMID: 11533209
- PMCID: PMC114514
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9470-9482.2001
A cellular J-domain protein modulates polyprotein processing and cytopathogenicity of a pestivirus
Abstract
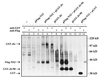
Pestiviruses are positive-strand RNA viruses closely related to human hepatitis C virus. Gene expression of these viruses occurs via translation of a polyprotein, which is further processed by cellular and viral proteases. Here we report the formation of a stable complex between an as-yet-undescribed cellular J-domain protein, a member of the DnaJ-chaperone family, and pestiviral nonstructural protein NS2. Accordingly, we termed the cellular protein Jiv, for J-domain protein interacting with viral protein. Jiv has the potential to induce in trans one specific processing step in the viral polyprotein, namely, cleavage of NS2-3. Efficient generation of its cleavage product NS3 has previously been shown to be obligatory for the cytopathogenicity of the pestiviruses. Regulated expression of Jiv in cells infected with noncytopathogenic bovine viral diarrhea virus disclosed a direct correlation between the intracellular level of Jiv, the extent of NS2-3 cleavage, and pestiviral cytopathogenicity.
Figures








References
-
- Collett M S, Larson R, Gold C, Strick D, Anderson D K, Purchio A F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the pestivirus bovine viral diarrhea virus. Virology. 1988;165:191–199. - PubMed
-
- Corapi W V, Donis R O, Dubovi E J. Characterization of a panel of monoclonal antibodies and their use in the study of the antigenic diversity of bovine viral diarrhea virus. Am J Vet Res. 1990;51:1388–1394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

