Interferon regulatory factor 4 contributes to transformation of v-Rel-expressing fibroblasts
- PMID: 11533227
- PMCID: PMC99785
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.19.6369-6386.2001
Interferon regulatory factor 4 contributes to transformation of v-Rel-expressing fibroblasts
Abstract
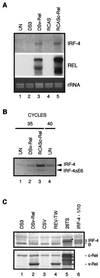
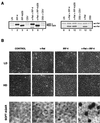
The avian homologue of the interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF-4) and a novel splice variant lacking exon 6, IRF-4DeltaE6, were isolated and characterized. Chicken IRF-4 is expressed in lymphoid organs, less in small intestine, and lungs. IRF-4DeltaE6 mRNA, though less abundant than full-length IRF-4, was detected in lymphoid tissues, with the highest levels observed in thymic cells. IRF-4 is highly expressed in v-Rel-transformed lymphocytes, and the expression of IRF-4 is increased in v-Rel- and c-Rel-transformed fibroblasts relative to control cells. The expression of IRF-4 from retrovirus vectors morphologically transformed primary fibroblasts, increased their saturation density, proliferation, and life span, and promoted their growth in soft agar. IRF-4 and v-Rel cooperated synergistically to transform fibroblasts. The expression of IRF-4 antisense RNA eliminated formation of soft agar colonies by v-Rel and reduced the proliferation of v-Rel-transformed cells. v-Rel-transformed fibroblasts produced interferon 1 (IFN1), which inhibits fibroblast proliferation. Infection of fibroblasts with retroviruses expressing v-Rel resulted in an increase in the mRNA levels of IFN1, the IFN receptor, STAT1, JAK1, and 2',5'-oligo(A) synthetase. The exogenous expression of IRF-4 in v-Rel-transformed fibroblasts decreased the production of IFN1 and suppressed the expression of several genes in the IFN transduction pathway. These results suggest that induction of IRF-4 expression by v-Rel likely facilitates transformation of fibroblasts by decreasing the induction of this antiproliferative pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel interferon regulatory factor (IRF), IRF-10, has a unique role in immune defense and is induced by the v-Rel oncoprotein.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(11):3942-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.11.3942-3957.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11997525 Free PMC article.
-
Avian I kappa B alpha is transcriptionally induced by c-Rel and v-Rel with different kinetics.J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5383-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.9.5383-5390.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7636983 Free PMC article.
-
AP-1 factors play an important role in transformation induced by the v-rel oncogene.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2997-3009. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2997. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9566919 Free PMC article.
-
The growing family of interferon regulatory factors.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997 Dec;8(4):293-312. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(97)00019-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997. PMID: 9620643 Review.
-
Enhancement and diversification of IFN induction by IRF-7-mediated positive feedback.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 Jan;22(1):87-93. doi: 10.1089/107999002753452692. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 11846979 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of the inhibitor of apoptosis ch-IAP1 by v-rel and the proto-oncogene c-rel.J Virol. 2002 Dec;76(23):11960-70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.23.11960-11970.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12414938 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors and regulation of oncogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2008 Mar;99(3):467-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00720.x. Epub 2008 Jan 9. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18190617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of ATF2 in Rel/NFκB oncogenesis reveals its role in the regulation of Ras signaling.Small GTPases. 2011 Mar;2(2):89-94. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.2.2.15310. Small GTPases. 2011. PMID: 21776408 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of B-cell linker (BLNK) and B-cell adaptor for phosphoinositide 3-kinase (BCAP) is important for lymphocyte transformation by rel proteins.Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 1;68(3):808-14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3169. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18245482 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of telomerase activation by v-Rel and its contribution to transformation.J Virol. 2006 Jan;80(1):281-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.1.281-295.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16352553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbadie C, Kabrun N, Bouali F, Smardova J, Stehelin D, Vandenbunder B, Enrietto P J. High levels of c-relexpression are associated with programmed cell death in the developing avian embryo and in bone marrow cells in vitro. Cell. 1993;75:899–912. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama Y, Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974;17:105–116. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
