ETO, a target of t(8;21) in acute leukemia, makes distinct contacts with multiple histone deacetylases and binds mSin3A through its oligomerization domain
- PMID: 11533236
- PMCID: PMC99794
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.19.6470-6483.2001
ETO, a target of t(8;21) in acute leukemia, makes distinct contacts with multiple histone deacetylases and binds mSin3A through its oligomerization domain
Abstract
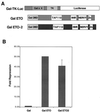
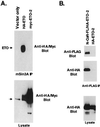
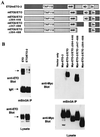
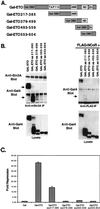
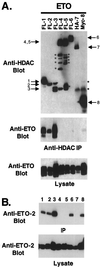
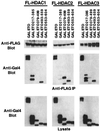
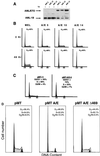
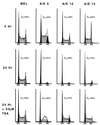
t(8;21) and t(16;21) create two fusion proteins, AML-1-ETO and AML-1-MTG16, respectively, which fuse the AML-1 DNA binding domain to putative transcriptional corepressors, ETO and MTG16. Here, we show that distinct domains of ETO contact the mSin3A and N-CoR corepressors and define two binding sites within ETO for each of these corepressors. In addition, of eight histone deacetylases (HDACs) tested, only the class I HDACs HDAC-1, HDAC-2, and HDAC-3 bind ETO. However, these HDACs bind ETO through different domains. We also show that the murine homologue of MTG16, ETO-2, is also a transcriptional corepressor that works through a similar but distinct mechanism. Like ETO, ETO-2 interacts with N-CoR, but ETO-2 fails to bind mSin3A. Furthermore, ETO-2 binds HDAC-1, HDAC-2, and HDAC-3 but also interacts with HDAC-6 and HDAC-8. In addition, we show that expression of AML-1-ETO causes disruption of the cell cycle in the G(1) phase. Disruption of the cell cycle required the ability of AML-1-ETO to repress transcription because a mutant of AML-1-ETO, Delta469, which removes the majority of the corepressor binding sites, had no phenotype. Moreover, treatment of AML-1-ETO-expressing cells with trichostatin A, an HDAC inhibitor, restored cell cycle control. Thus, AML-1-ETO makes distinct contacts with multiple HDACs and an HDAC inhibitor biologically inactivates this fusion protein.
Figures



References
-
- Ahn M Y, Huang G, Bae S C, Wee H J, Kim W Y, Ito Y. Negative regulation of granulocytic differentiation in the myeloid precursor cell line 32Dcl3 by ear-2, a mammalian homolog of Drosophila seven-up, and a chimeric leukemogenic gene, AML1/ETO. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:1812–1817. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao W, Britos-Bray M, Claxton D F, Kelley C A, Speck N A, Liu P P, Friedman A D. CBF beta-SMMHC, expressed in M4Eo AML, reduced CBF DNA-binding and inhibited the G1 to S cell cycle transition at the restriction point in myeloid and lymphoid cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:1315–1327. - PubMed
-
- Davis J N, Williams B J, Herron J T, Galiano F J, Meyers S. ETO-2: a new member of the ETO-family of nuclear proteins. Oncogene. 1999;18:1375–1383. - PubMed
-
- Erickson P, Gao J, Chang K S, Look T, Whisenant E, Raimondi S, Lasher R, Trujillo J, Rowley J, Drabkin H. Identification of breakpoints in t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia and isolation of a fusion transcript, AML1/ETO, with similarity to Drosophila segmentation gene, runt. Blood. 1992;80:1825–1831. - PubMed
-
- Erickson P F, Robinson M, Owens G, Drabkin H A. The ETO portion of acute myeloid leukemia t(8;21) fusion transcript encodes a highly evolutionarily conserved, putative transcription factor. Cancer Res. 1994;54:1782–1786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
