ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini
- PMID: 11533657
- PMCID: PMC2952547
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb0901-785
ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini
Abstract
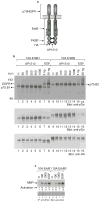
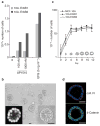
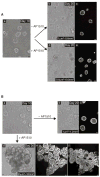
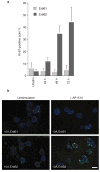
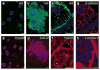
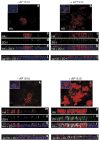
Both ErbB1 and ErbB2 are overexpressed or amplified in breast tumours. To examine the effects of activating ErbB receptors in a context that mimics polarized epithelial cells in vivo, we activated ErbB1 and ErbB2 homodimers in preformed, growth-arrested mammary acini cultured in three-dimensional basement membrane gels. Activation of ErbB2, but not that of ErbB1, led to a reinitiation of cell proliferation and altered the properties of mammary acinar structures. These altered structures share several properties with early-stage tumours, including a loss of proliferative suppression, an absence of lumen, retention of the basement membrane and a lack of invasive properties. ErbB2 activation also disrupted tight junctions and the cell polarity of polarized epithelia, whereas ErbB1 activation did not have any effect. Our results indicate that ErbB receptors differ in their ability to induce early stages of mammary carcinogenesis in vitro and this three-dimensional model system can reveal biological activities of oncogenes that cannot be examined in vitro in standard transformation assays.
Figures
References
-
- Petersen OW, Ronnov-Jessen L, Howlett AR, Bissell MJ. Interaction with basement membrane serves to rapidly distinguish growth and differentiation pattern of normal and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:9064–9068. (Erratum, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA90, 2556 (1993).) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris J, Lippman M, Morrow M, Osborne C. Diseases of the Breast. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Philadelphia: 1999.
-
- Riese DJ, 2nd, Stern DF. Specificity within the EGF family/ErbB receptor family signaling network. BioEssays. 1998;20:41–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

