Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, a genodermatosis associated with spontaneous pneumothorax and kidney neoplasia, maps to chromosome 17p11.2
- PMID: 11533913
- PMCID: PMC1226073
- DOI: 10.1086/323744
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, a genodermatosis associated with spontaneous pneumothorax and kidney neoplasia, maps to chromosome 17p11.2
Abstract
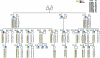
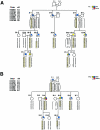
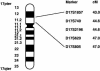
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHD), an inherited autosomal genodermatosis characterized by benign tumors of the hair follicle, has been associated with renal neoplasia, lung cysts, and spontaneous pneumothorax. To identify the BHD locus, we recruited families with cutaneous lesions and associated phenotypic features of the BHD syndrome. We performed a genomewide scan in one large kindred with BHD and, by linkage analysis, localized the gene locus to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 17p, with a LOD score of 4.98 at D17S740 (recombination fraction 0). Two-point linkage analysis of eight additional families with BHD produced a maximum LOD score of 16.06 at D17S2196. Haplotype analysis identified critical recombinants and defined the minimal region of nonrecombination as being within a <4-cM distance between D17S1857 and D17S805. One additional family, which had histologically proved fibrofolliculomas, did not show evidence of linkage to chromosome 17p, suggesting genetic heterogeneity for BHD. The BHD locus lies within chromosomal band 17p11.2, a genomic region that, because of the presence of low-copy-number repeat elements, is unstable and that is associated with a number of diseases. Identification of the gene for BHD may reveal a new genetic locus responsible for renal neoplasia and for lung and hair-follicle developmental defects.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics (for map distances)
-
- UCSC Human Genome Project Working Draft, http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hgTracks.html (for Human Genome Browser, version 4 [“Golden Path”])
References
-
- Birt AR, Hogg GR, Dubé WJ (1977) Hereditary multiple fibrofolliculomas with trichodiscomas and acrochordons. Arch Dermatol 113:1674–1677 - PubMed
-
- Chen KS, Gunaratne PH, Hoheisel JD, Young IG, Miklos GL, Greenberg F, Shaffer LG, Campbell HD, Lupski JR (1995) The human homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster flightless-I gene (fli1) maps within the Smith-Magenis microdeletion critical region in 17p11.2. Am J Hum Genet 56:175–182 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen KS, Potocki L, Lupski JR (1996) The Smith-Magenis syndrome [del(17)p11.2]: critical review and molecular advances. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 2:122–129
-
- Chen KS, Manian P, Koeuth T, Potocki L, Zhao Q, Chinault AC, Lee CC, Lupski J (1997) Homologous recombination of a flanking repeat gene cluster is a mechanism for a common contiguous gene deletion syndrome. Nat Genet 17:154–163 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

