Functionalized xenon as a biosensor
- PMID: 11535830
- PMCID: PMC58521
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.191368398
Functionalized xenon as a biosensor
Abstract
The detection of biological molecules and their interactions is a significant component of modern biomedical research. In current biosensor technologies, simultaneous detection is limited to a small number of analytes by the spectral overlap of their signals. We have developed an NMR-based xenon biosensor that capitalizes on the enhanced signal-to-noise, spectral simplicity, and chemical-shift sensitivity of laser-polarized xenon to detect specific biomolecules at the level of tens of nanomoles. We present results using xenon "functionalized" by a biotin-modified supramolecular cage to detect biotin-avidin binding. This biosensor methodology can be extended to a multiplexing assay for multiple analytes.
Figures


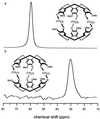

References
-
- Malmqvist M. Nature (London) 1993;361:186–187. - PubMed
-
- Checovich W J, Bolger R E, Burke T. Nature (London) 1995;375:254–256. - PubMed
-
- Miyawaki A, Llopis J, Heim R, McCaffery J M, Adams J A, Ikura M, Tsien R Y. Nature (London) 1997;388:882–887. - PubMed
-
- Shuker S B, Hajduk P J, Meadows R P, Fesik S W. Science. 1996;274:1531–1534. - PubMed
-
- Louie A Y, Huber M M, Ahrens E T, Rothbacher U, Moats R, Jacobs R E, Fraser S E, Meade T J. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:321–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

