Growth retardation and increased apoptosis in mice with homozygous disruption of the Akt1 gene
- PMID: 11544177
- PMCID: PMC312770
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.913901
Growth retardation and increased apoptosis in mice with homozygous disruption of the Akt1 gene
Abstract
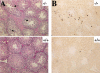
The serine/threonine kinase Akt has been implicated in the control of cell survival and metabolism. Here we report the disruption of the most ubiquitously expressed member of the akt family of genes, akt1, in the mouse. Akt1(-/-) mice are viable but smaller when compared to wild-type littermates. In addition, the life span of Akt1(-/-) mice, upon exposure to genotoxic stress, is shorter. However, Akt1(-/-) mice do not display a diabetic phenotype. Increased spontaneous apoptosis in testes, and attenuation of spermatogenesis is observed in Akt1(-/-) male mice. Increased spontaneous apoptosis is also observed in the thymi of Akt1(-/-) mice, and Akt1(-/-) thymocytes are more sensitive to apoptosis induced by gamma-irradiation and dexamethasone. Finally, Akt1(-/-) mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) are more susceptible to apoptosis induced by TNF, anti-Fas, UV irradiation, and serum withdrawal.
Figures







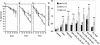
References
-
- Alessi DR, Cohen P. Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Altomare DA, Guo K, Cheng JQ, Sonoda G, Walsh K, Testa JR. Cloning, chromosomal localization and expression analysis of the mouse Akt2 oncogene. Oncogene. 1995;11:1055–1060. - PubMed
-
- Altomare DA, Lyons GE, Mitsuuchi Y, Cheng JQ, Testa JR. Akt2 mRNA is highly expressed in embryonic brown fat and the AKT2 kinase is activated by insulin. Oncogene. 1998;116:2407–2411. - PubMed
-
- Barthel A, Okino ST, Liao J, Nakatani K, Li J, Whitlock J, Jr, Roth RA. Regulation of GLUT1 gene transcription by the serine/threonine kinase Akt1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20281–20286. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Jiang G, Hyman R, Lee KF, O'Gorman S, Hunter T. Kit/stem cell factor receptor-induced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase is essential for male fertility. Nat Genet. 2000;24:157–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
