LuxArray, a high-density, genomewide transcription analysis of Escherichia coli using bioluminescent reporter strains
- PMID: 11544210
- PMCID: PMC95439
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.183.19.5496-5505.2001
LuxArray, a high-density, genomewide transcription analysis of Escherichia coli using bioluminescent reporter strains
Abstract
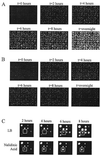
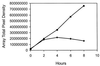
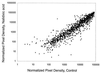
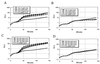
A sequenced collection of plasmid-borne random fusions of Escherichia coli DNA to a Photorhabdus luminescens luxCDABE reporter was used as a starting point to select a set of 689 nonredundant functional gene fusions. This group, called LuxArray 1.0, represented 27% of the predicted transcriptional units in E. coli. High-density printing of the LuxArray 1.0 reporter strains to membranes on agar plates was used for simultaneous reporter gene assays of gene expression. The cellular response to nalidixic acid perturbation was analyzed using this format. As expected, fusions to promoters of LexA-controlled SOS-responsive genes dinG, dinB, uvrA, and ydjM were found to be upregulated in the presence of nalidixic acid. In addition, six fusions to genes not previously known to be induced by nalidixic acid were also reproducibly upregulated. The responses of two of these, fusions to oraA and yigN, were induced in a LexA-dependent manner by both nalidixic acid and mitomycin C, identifying these as members of the LexA regulon. The responses of the other four were neither induced by mitomycin C nor dependent on lexA function. Thus, the promoters of ycgH, intG, rihC, and a putative operon consisting of lpxA, lpxB, rnhB, and dnaE were not generally DNA damage responsive and represent a more specific response to nalidixic acid. These results demonstrate that cellular arrays of reporter gene fusions are an important alternative to DNA arrays for genomewide transcriptional analyses.
Figures
References
-
- Arfin S M, Long A D, Ito E T, Tolleri L, Riehle M M, Paegle E S, Hatfield G W. Global gene expression profiling in Escherichia coli K12: the effects of integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:29672–29684. - PubMed
-
- Belkin S, Smulski D R, Dadon S, Vollmer A C, Van Dyk T K, LaRossa R A. A panel of stress-responsive luminous bacteria for the detection of selected classes of toxicants. Water Res. 1997;31:3009–3016.
-
- Blattner F R, Plunkett III G, Bloch C A, Perna N T, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner J D, Rode C K, Mayhew G F, Gregor J, Davis N W, Kirkpatrick H A, Goeden M A, Rose D J, Mau B, Shao Y. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1462. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee J, Meighen E A. Biotechnological applications of bacterial bioluminescence (lux) genes. Photochem Photobiol. 1995;62:641–650.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

