Effect of targeted disruption of STAT4 and STAT6 on the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 11544280
- PMCID: PMC209380
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12563
Effect of targeted disruption of STAT4 and STAT6 on the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
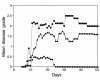
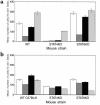
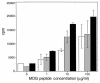
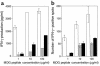
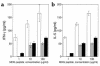
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is mediated by myelin-specific CD4(+) T cells secreting Th1 cytokines, while recovery from disease is associated with expression of Th2 cytokines. Investigations into the role of individual cytokines in disease induction have yielded contradictory results. Here we used animals with targeted deletion of the STAT4 or STAT6 genes to determine the role of these signaling molecules in EAE. The STAT4 pathway controls the differentiation of cells into a Th1 phenotype, while the STAT6 pathway controls the differentiation of cells into a Th2 phenotype. We found that mice deficient in STAT4 are resistant to the induction of EAE, with minimal inflammatory infiltrates in the central nervous system. In contrast, STAT6-deficient mice, which have a predominantly Th1 phenotype, experience a more severe clinical course of EAE as compared with wild-type or STAT4 knockout mice. In addition, adoptive transfer studies confirm the regulatory functions of a Th2 environment in vivo. These novel data indicate that STAT4 and STAT6 genes play a critical role in regulating the autoimmune response in EAE.
Figures
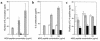
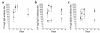


References
-
- Powell MB, et al. Lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by myelin basic protein-specific T cell clones correlates with encephalitogenicity. Int Immunol. 1990;2:539–544. - PubMed
-
- Begolka WS, Vanderlugt CL, Rahbe SM, Miller SD. Differential expression of inflammatory cytokines parallels progression of central nervous system pathology in two clinically distinct models of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 1998;161:4437–4446. - PubMed
-
- Issazadeh S, Ljungdahl A, Hojeberg B, Mustafa M, Olsson T. Cytokine production in the central nervous system of Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: dynamics of mRNA expression for interleukin-10, interleukin-12, cytolysin, tumor necrosis factor alpha and tumor necrosis factor beta. J Neuroimmunol. 1995;61:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Issazadeh S, Navikas V, Schaub M, Sayegh M, Khoury S. Kinetics of expression of costimulatory molecules and their ligands in murine relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in vivo. J Immunol. 1998;161:1104–1112. - PubMed
-
- Khoury SJ, Hancock WW, Weiner HL. Oral tolerance to myelin basic protein and natural recovery from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are associated with downregulation of inflammatory cytokines and differential upregulation of transforming growth factor beta, interleukin 4, and prostaglandin E expression in the brain. J Exp Med. 1992;176:1355–1364. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

