An antagonist IL-15/Fc protein prevents costimulation blockade-resistant rejection
- PMID: 11544341
- PMCID: PMC3806296
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.6.3478
An antagonist IL-15/Fc protein prevents costimulation blockade-resistant rejection
Abstract
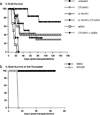
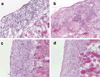
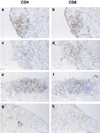
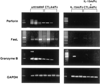
IL-15 is a powerful T cell growth factor (TCGF) with particular importance for the maintenance of CD8(+) T cells. Because costimulation blockade does not result in universal tolerance, we hypothesized that "escape" from costimulation blockade might represent a CD8(+) and IL-15/IL-15R(+)-dependent process. For this analysis, we have used an IL-15 mutant/Fcgamma2a protein, a potentially cytolytic protein that is also a high-affinity receptor site specific antagonist for the IL-15Ralpha receptor protein, as a therapeutic agent. The IL-15-related fusion protein was used as monotherapy or in combination with CTLA4/Fc in murine islet allograft models. As monotherapies, CTLA4/Fc and an IL-15 mutant/Fcgamma2a were comparably effective in a semiallogeneic model system, and combined treatment with IL-15 mutant/Fcgamma2a plus CTLA4/Fc produced universal permanent engraftment. In a fully MHC-mismatched strain combination known to be refractory to costimulation blockade treatment, combined treatment with both fusion proteins proved to be highly effective; >70% of recipients were tolerized. The analysis revealed that the IL-15 mutant/Fc treatment confers partial protection from both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell graft infiltration. In rejections occurring despite CTLA4/Fc treatment, concomitant treatment with the IL-15 mutant/Fcgamma2a protein blocked a CD8(+) T cell-dominated rejection processes. This protection was linked to a blunted proliferative response of alloreactive T cells as well silencing of CTL-related gene expression events. Hence, we have demonstrated that targeting the IL-15/IL-15R pathway represents a new and potent strategy to prevent costimulation blockade-resistant CD8(+) T cell-driven rejection.
Figures
References
-
- June CH, Bluestone JA, Nadler LM, Thompson CB. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol. Today. 1994;15:321. - PubMed
-
- Lenschow DJ, Walunas TL, Bluestone JA. CD28/B7 system of T-cell costimulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:233. - PubMed
-
- Grewal IS, Flavell RA. CD40 and CD154 in cell mediated immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998;16:111. R. A. - PubMed
-
- Marengere LE, Waterhouse P, Duncan GS, Mittrucker H-W, Feng GS, Mak TW. Regulation of T cell receptor signaling by tyrosine phosphatase in association with CTLA-4. Science. 1996;272:1170. - PubMed
-
- Lenschow DJ, Zeng Y, Thistlethwaite JR, Montag A, Brady W, Gibson MG, Linsley PS, Bluestone JA. Long-term survival of xenogeneic pancreatic islet grafts induced by CTLA4Ig. Science. 1992;257:789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

