Significance of interferon-gamma in coronary artery bypass surgery
- PMID: 11548832
- PMCID: PMC3015452
Significance of interferon-gamma in coronary artery bypass surgery
Abstract
Background: Gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) is produced by activated natural killer and T cells under pathologic circumstances. The objective of our study was to compare the level of IFN-gamma in open and endoscopic methods of vein harvesting for coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
Method: Ninety samples of human saphenous veins harvested from patients prepared for CABG. Pre- and post-procedure sera of the patients, in addition to supernatants of 3-day endothelial cell culture, were analyzed for IFN-gamma.
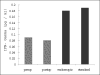
Results: The mean preoperative IFN-gamma level (0.09+/-0.03 pg/mL) and that for postoperative sera (0.08+/-0.02 pg/mL) were not significantly different (P = 0.2). The mean IFN-gamma level in endothelial cell culture from the endoscopic (0.18+/-0.21 pg/mL) and the open method (0.19+/-0.39 pg/mL) were not significant (P = 0.89).
Conclusion: We recommend the endoscopic method of vein harvesting because of its lower morbidity and earlier hospital discharge.
Figures
References
-
- Holzinger C, Weissinger E, Zuckermann A, et al. Effects of interleukin-1,-2,-4,-6, and interferon gamma and granulocyte /macrophage colony stimulating factor on human vascular endothelial cells. Immunol Lett. 1993; 35: 109–118 - PubMed
-
- Harlan JM. Leukocyte-endothelial interaction. Blood. 1985; 65: 513. - PubMed
-
- Ruszczak Z, Detmar M, Imcke E, Orfan CE. Effects of rIFN Alpha, Beta, and Gamma on the morphology, proliferation, and cell surface antigen expression of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Soc Invest Dermatol. 1990; 95: 693–699 - PubMed
-
- Cotran RS, Pober JS. Effects of cytokines on vascular endothelium: their role in vascular and immune injury. Kidney Int. 1989; 35: 969–975 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical