Fibroblast heterogeneity: existence of functionally distinct Thy 1(+) and Thy 1(-) human female reproductive tract fibroblasts
- PMID: 11549585
- PMCID: PMC1850439
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61768-3
Fibroblast heterogeneity: existence of functionally distinct Thy 1(+) and Thy 1(-) human female reproductive tract fibroblasts
Abstract
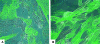
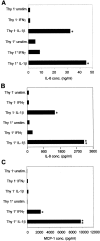
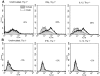
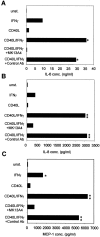
Little is known about fibroblasts from the female reproductive tract, much less whether or not functional subsets exist. Fibroblasts are key as sentinel cells for recruiting white blood cells and for wound healing. The purpose of this research was to evaluate the possibility that functional subsets of fibroblasts exist in the human female reproductive tract. The strategy used was to define fibroblast subpopulations based on their surface expression of the Thy 1 antigen. In situ staining of human myometrium and endometrium showed heterogeneous staining for Thy 1. Freshly derived strains of fibroblasts from the myometrium and endometrium also demonstrated heterogeneous Thy 1 expression. For the first time, using magnetic beading and fluorescence-activated cell sorting, human myometrial fibroblasts were successfully separated into functionally unique Thy 1(+) and Thy 1(-) subsets. Both subsets produced the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 after IL-1beta stimulation, but only the Thy 1(+) subset produced MCP-1. Furthermore, only Thy 1(+) fibroblasts up-regulated CD40 surface expression with IL-1beta or interferon-gamma treatment. Engagement of CD40 in the Thy 1(+) subpopulation induced IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1. The discovery of functional subsets of reproductive tract fibroblasts now permits assessment of their roles in the normal functions of the reproductive tract and in disease states such as adhesions and menorrhagia.
Figures


References
-
- Kelly RW: Pregnancy maintenance and parturition: the role of prostaglandin in manipulating the immune and inflammatory response. Endocr Rev 1994, 15:684-706 - PubMed
-
- Thomson AJ, Telfer JF, Young A, Campbell S, Stewart CJ, Cameron IT, Greer IA, Norman JE: Leukocytes infiltrate the myometrium during human parturition: further evidence that labour is an inflammatory process. Hum Reprod 1999, 14:229-236 - PubMed
-
- Gaspari AA, Sempowski GD, Chess P, Gish J, Phipps RP: Human epidermal keratinocytes are induced to secrete interleukin-6 and co-stimulate T lymphocyte proliferation by a CD40-dependent mechanism. Eur J Immunol 1996, 26:1371-1377 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

