Endothelial oxidative stress activates the lectin complement pathway: role of cytokeratin 1
- PMID: 11549596
- PMCID: PMC1850443
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61779-8
Endothelial oxidative stress activates the lectin complement pathway: role of cytokeratin 1
Abstract
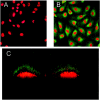
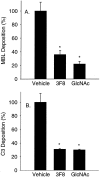
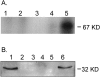
Oxidative stress increases endothelial mannose-binding lectin (MBL) binding and activates the lectin complement pathway (LCP). However, the molecular mechanism of MBL binding to the endothelium after oxidative stress is unknown. Intermediate filaments have been previously reported to activate the classical complement pathway in an antibody-independent manner. We investigated whether oxidative stress increases human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) cytokeratin 1 (CK1) expression and activates the LCP via MBL binding to CK1. Reoxygenation (3 hours, 21% O(2)) of hypoxic HUVECs (24 hours, 1% O(2)) significantly increased CK1 mRNA (in situ hybridization) and membrane protein expression [enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)/confocal microscopy]. Incubating human serum (HS) with N-acetyl-D-glucosamine or anti-human MBL monoclonal antibody attenuated MBL and C3 deposition on purified CK1 (ELISA). CK1 and MBL were co-immunoprecipitated from hypoxic HUVECs reoxygenated in HS. Treatment with anti-human cytokeratin Fab fragments attenuated endothelial MBL and C3 deposition after oxidative stress (ELISA/confocal microscopy). We conclude that: 1) endothelial oxidative stress increases CK1 expression, MBL binding, and C3 deposition; 2) inhibition of MBL attenuates purified CK1-induced complement activation; and 3) anti-human cytokeratin Fab fragments attenuate endothelial MBL and C3 deposition after oxidative stress. These results suggest that MBL binding to endothelial cytokeratins may mediate LCP activation after oxidative stress.
Figures




References
-
- Thiel S, Vorup-Jensen T, Stover CM, Schwaeble W, Laursen SB, Poulsen K, Willis AC, Eggleton P, Hansen S, Holmskov U, Reid KB, Jensenius JC: A second serine protease associated with mannan-binding lectin that activates complement. Nature 1997, 386:506-510 - PubMed
-
- Turner MW: The lectin pathway of complement activation. Res Immunol 1996, 147:110-115 - PubMed
-
- Turner MW: Mannose-binding lectin: the pluripotent molecule of the innate immune system. Immunol Today 1996, 17:532-540 - PubMed
-
- Turner MW: Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in health and disease. Immunobiology 1998, 199:327-339 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

