Thrombin regulates chemokine induction during human retinal pigment epithelial cell/monocyte interaction
- PMID: 11549610
- PMCID: PMC1850462
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61793-2
Thrombin regulates chemokine induction during human retinal pigment epithelial cell/monocyte interaction
Abstract
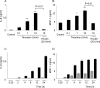
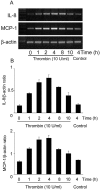
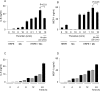
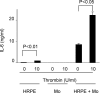
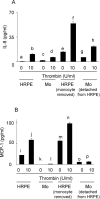
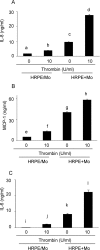
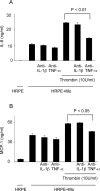
Thrombin, an important clotting factor, extravasates at sites of blood-retina barrier breakdown that is often associated with many retinal diseases. Here we investigated the effects of thrombin on human retinal pigment epithelial (HRPE) cells, monocytes, and HRPE cell/monocyte co-cultures. Thrombin induced secretion and mRNA expression of HRPE interleukin (IL)-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). Thrombin also enhanced IL-8 and MCP-1 by HRPE cell/monocyte co-cultures, by apparently enhancing cell-cell contact mechanisms. The thrombin effects on IL-6 secretion were similar to those on chemokine secretion. Thrombin-induced chemokines by co-cultures were inhibited by anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) antibody, but not by anti-IL-1beta antibody. TNF-alpha was detected in cell lysates of monocytes detached from HRPE cells after co-culture stimulation with thrombin. HRPE cells mainly produced these chemokines. However, thrombin generally potentiated exogenous IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-induced chemokine production by HRPE cells, monocytes, and co-cultures. Interferon-gamma potentiated chemokine secretion by co-cultures with or without thrombin. Our results indicate that thrombin may cause leukocyte recruitment by inducing HRPE cell and monocyte chemokine and by enhancing HRPE cell/monocyte interactions, in part because of monocyte TNF-alpha induction, suggesting important mechanisms for ocular inflammation during blood-retina barrier breakdown and intra-ocular hemorrhage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential chemokine regulation by Th2 cytokines during human RPE-monocyte coculture.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001 Jun;42(7):1631-8. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001. PMID: 11381071
-
Activation of p38, ERK1/2 and NIK pathways is required for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha-induced chemokine expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2001 Jul;73(1):111-21. doi: 10.1006/exer.2001.1019. Exp Eye Res. 2001. PMID: 11428868
-
Human retinal pigment epithelial cell interleukin-8 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 modulation by T-lymphocyte products.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997 Feb;38(2):446-55. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997. PMID: 9040478
-
Cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions mediate chemokine expression: an important component of the inflammatory lesion.J Leukoc Biol. 1997 Nov;62(5):612-9. doi: 10.1002/jlb.62.5.612. J Leukoc Biol. 1997. PMID: 9365116 Review.
-
Some aspects of IL-8 pathophysiology. III: Chemokine interaction with endothelial cells.J Leukoc Biol. 1996 Jan;59(1):39-44. doi: 10.1002/jlb.59.1.39. J Leukoc Biol. 1996. PMID: 8558065 Review.
Cited by
-
The kinetics of VEGF and MCP-1 in the second vitrectomy cases with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.Eye (Lond). 2016 May;30(5):746-53. doi: 10.1038/eye.2016.20. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Eye (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26915745 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin-induced VEGF expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Jun;48(6):2738-46. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-1023. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17525207 Free PMC article.
-
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) induces FasL and reduces iNOS and Cox2 in primary monocytes.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Nov;252(11):1747-54. doi: 10.1007/s00417-014-2742-z. Epub 2014 Jul 25. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25059476
-
MCP-1-activated monocytes induce apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelium.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Jul 29;52(8):6026-34. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-7023. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21447688 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Blood Coagulation Factor X (FXa) Contributes to the Development of Traumatic PVR Through Promoting RPE Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):29. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.29. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34283209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vinores SA, Amin A, Derevjanik NL, Green WR, Campochiaro PA: Immunohistochemical localization of blood-retinal barrier breakdown sites associated with post-surgical macular oedema. Histochem J 1994, 26:655-665 - PubMed
-
- Bamforth SD, Lightman S, Greenwood J: The effect of TNF-alpha and IL-6 on the permeability of the rat blood-retinal barrier in vivo. Acta Neuropathol 1996, 91:624-632 - PubMed
-
- Sen HA, Robertson TJ, Conway BP, Campochiaro PA: The role of breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in cell-injection models of proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 1988, 106:1291-1294 - PubMed
-
- Fenton JW, Fasco MJ, Stackrow AB: Human thrombins. Production, evaluation, and properties of alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem 1977, 252:3587-3598 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

