Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors produces a direct excitation and disinhibition of GABAergic projection neurons in the substantia nigra pars reticulata
- PMID: 11549710
- PMCID: PMC6762993
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07001.2001
Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors produces a direct excitation and disinhibition of GABAergic projection neurons in the substantia nigra pars reticulata
Abstract
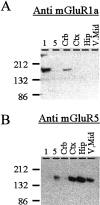
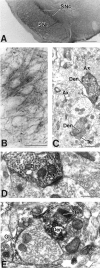
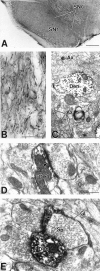
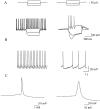
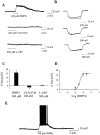
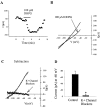
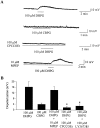
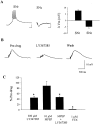
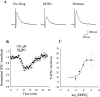
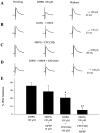
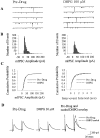
A pathological increase in excitatory glutamatergic input to substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) from the subthalamic nucleus (STN) is believed to play a key role in the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. We present an analysis of the physiological roles that group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) play in regulating SNr functions. Immunocytochemical analysis at the light and electron microscopic levels reveal that both mGuR1a and mGluR5 are localized postsynaptically in the SNr. Consistent with this, activation of group I mGluRs depolarizes SNr GABAergic neurons. Interestingly, although both group I mGluRs (mGluR1 and mGluR5) are expressed in these neurons, the effect is mediated solely by mGluR1. Light presynaptic staining for mGluR1a and mGluR5 was also observed in some terminals forming symmetric synapses and in small unmyelinated axons. Consistent with this, activation of presynaptic mGluR1a and mGluR5 decreases inhibitory transmission in the SNr. The combination of direct excitatory effects and disinhibition induced by activation of group I mGluRs could lead to a large excitation of SNr projection neurons. This suggests that group I mGluRs are likely to play an important role in the powerful excitatory control that the STN exerts on basal ganglia output neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 inhibits glutamatergic transmission in the substantia nigra pars reticulata.Neuroscience. 2001;105(4):881-9. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00254-8. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11530226
-
Activation of group III mGluRs inhibits GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission in the substantia nigra pars reticulata.J Neurophysiol. 2001 May;85(5):1960-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.85.5.1960. J Neurophysiol. 2001. PMID: 11353013
-
Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 has direct excitatory effects and potentiates NMDA receptor currents in neurons of the subthalamic nucleus.J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 1;20(21):7871-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-21-07871.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11050106 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic and integrative properties of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons.Neuroscience. 2011 Dec 15;198:69-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.061. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21839148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the regulation of pancreatic functions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 15;87(4):535-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24355565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Germinated Brown Rice in Rotenone-Induced Parkinson's-Like Disease Rats.Neuromolecular Med. 2016 Sep;18(3):334-46. doi: 10.1007/s12017-016-8427-5. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Neuromolecular Med. 2016. PMID: 27430236
-
Localization and expression of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the mouse striatum, globus pallidus, and subthalamic nucleus: regulatory effects of MPTP treatment and constitutive Homer deletion.J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 6;27(23):6249-60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3819-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17553998 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functional roles of the metabotropic glutamate receptors 1 and 5 in the rat globus pallidus.J Neurosci. 2003 Jan 1;23(1):122-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-01-00122.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12514208 Free PMC article.
-
Differential subcellular localization of mGluR1a and mGluR5 in the rat and monkey Substantia nigra.J Neurosci. 2001 Mar 15;21(6):1838-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-01838.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11245668 Free PMC article.
-
The Biology and Pathobiology of Glutamatergic, Cholinergic, and Dopaminergic Signaling in the Aging Brain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 13;13:654931. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.654931. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34326765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott A, Wigmore MA, Lacey MG. Excitation of rat subthalamic nucleus neurones in vitro by activation of a group I metabotropic glutamate receptor. Brain Res. 1997;766:162–167. - PubMed
-
- Annoura H, Fukunaga A, Uesugi M, Tatsouka T, Horikawa Y. A novel class of antagonists for metabotropic glutamate receptors, 7-(hydroxyimino)cyclopropchromen-1a-carboxylates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1996;6:763–766.
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Awad H, Conn PJ. Regulation of neurons of thesubthalamic nucleus by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1999;25:176.15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
