Antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users: comparison of self-report and electronic monitoring
- PMID: 11550118
- PMCID: PMC2692641
- DOI: 10.1086/323201
Antiretroviral therapy adherence and viral suppression in HIV-infected drug users: comparison of self-report and electronic monitoring
Abstract
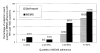
To compare electronically monitored (MEMS) with self-reported adherence in drug users, including the impact of adherence on HIV load, we conducted a 6-month observational study of 67 antiretroviral-experienced current and former drug users. Adherence (percentage of doses taken as prescribed) was calculated for both the day and the week preceding each of 6 research visits. Mean self-reported 1-day adherence was 79% (median, 86%), and mean self-reported 1-week adherence was 78% (median, 85%). Mean MEMS 1-day adherence was 57% (median, 52%), and mean MEMS 1-week adherence was 53% (median, 49%). One-day and 1-week estimates were highly correlated (r>.8 for both measures). Both self-reported and MEMS adherence were correlated with concurrent HIV load (r=.43-.60), but the likelihood of achieving virologic suppression was greater if MEMS adherence was high than if self-reported adherence was high. We conclude that self-reported adherence is higher than MEMS adherence, but a strong relationship exists between both measures and virus load. However, electronic monitoring is more sensitive than self-report for the detection of nonadherence and should be used in adherence intervention studies.
Figures
References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr., Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–60. - PubMed
-
- Hogg RS, Heath KV, Yip B, et al. Improved survival among HIV-infected individuals following initiation of antiretroviral therapy. JAMA. 1998;279:450–4. - PubMed
-
- Vanhove GF, Schapiro JM, Winters MA, Merigan TC, Blaschke TF. Patient compliance and drug failure in protease inhibitor monotherapy [letter] JAMA. 1996;6:1955–6. - PubMed
-
- Montaner JSG, Reiss P, Cooper D, et al. A randomized, double-blind trial comparing combinations of nevirapine, didanosine, and zidovudine for HIV-infected patients. JAMA. 1998;279:930–7. - PubMed
-
- Descamps D, Flandre P, Calvez V, et al. Mechanisms of virologic failure in previously untreated HIV-infected patients from a trial of induction-maintenance therapy. JAMA. 2000;283:205–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical