Molecular evolution of large virulence plasmid in Shigella clones and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli
- PMID: 11553574
- PMCID: PMC98765
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6303-6309.2001
Molecular evolution of large virulence plasmid in Shigella clones and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli
Abstract
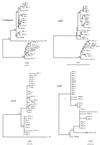
Three genes, ipgD, mxiC, and mxiA, all in the invasion region of the Shigella virulence plasmid, were sequenced from strains representing a range of Shigella serotypes and from two enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) isolates. The plasmids can be classified into two relatively homogeneous sequence forms which are quite distinct. pINV A plasmids are found in Shigella flexneri strains F6 and F6A, S. boydii strains B1, B4, B9, B10, B14, and B15, S. dysenteriae strains D3, D4, D6, D8, D9, D10, and D13, and the two EIEC strains (M519 and M520). pINV B plasmids are present in S. flexneri strains F1A, F2A, F3A, F3C, F4A, and FY, two S. boydii strains (B11 and B12), and S. sonnei. The D1 pINV plasmid is a recombinant with ipgD gene more closely related to those of pINV A but with mxiA and mxiC genes more closely related to those of pINV B. The phylogenetic relationships of the plasmid and those of the chromosomal genes of Shigella strains are largely consistent. The cluster 1 and cluster 3 strains tested (G.M. Pupo, R. Lan, and P. R. Reeves, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:10567-10572, 2000) have pINV A and pINV B plasmids, respectively. However, of the three cluster 2 strains (B9, B11, and B15), B9 and B15 have pINV A while B11 has a pINV B plasmid. Those Shigella (D8 and D10 and S. sonnei) and EIEC strains which do not group with the main body of Shigella strains based on chromosomal genes were found to have plasmids belonging to one or the other of the two types and must have acquired these by lateral transfer.
Figures

References
-
- Acheson D W K, Keusch G T. Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. In: Blaser M J, Smith P D, Ravdin J I, Greenberg H B, Guerrant R L, editors. Infections of the gastrointestinal tract. New York, N.Y: Raven Press; 1995. pp. 763–784.
-
- Al-Hassan K, Rajakumar K, Bulach D, Robbins-Browne R, Adler B, Sakellaris H. Genetic organization of the she pathogenicity island in Shigella flexneri 2a. Microb Pathog. 2001;30:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

