Bartonella henselae-specific cell-mediated immune responses display a predominantly Th1 phenotype in experimentally infected C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 11553587
- PMCID: PMC98778
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6427-6433.2001
Bartonella henselae-specific cell-mediated immune responses display a predominantly Th1 phenotype in experimentally infected C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
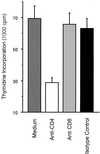
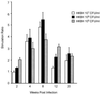
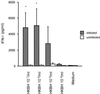
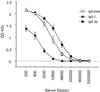
Immune responses of the immunocompetent host to Bartonella henselae infection were investigated in the murine infection model using C57BL/6 mice. Following intraperitoneal infection with human-derived B. henselae strain Berlin-1, viable bacteria could be recovered from livers and spleens during the first week postinfection, while Bartonella DNA remained detectable by PCR in the liver for up to 12 weeks after infection. Granulomatous lesions developed in livers of infected mice, reached maximal density at 12 weeks after infection, and persisted for up to 20 weeks, indicating that B. henselae induced a chronic granulomatous hepatitis in the immunocompetent murine host. T-cell-mediated immune responses were analyzed in vitro by means of spleen cell proliferation and cytokine release assays as well as analysis of immunoglobulin G (IgG) isotypes. Spleen cells from infected mice proliferated specifically upon stimulation with heat-killed Bartonella antigen. Proliferative responses were mainly mediated by CD4+ T cells, increased during the course of infection, peaked at 8 weeks postinfection, and decreased thereafter. Gamma interferon, but not interleukin-4, was produced in vitro by spleen cells from infected animals upon stimulation with Bartonella antigens. Bartonella-specific IgG was detectable in serum of infected mice by 2 weeks, and the antibody concentration peaked at 12 weeks postinfection. IgG2b was the prominent isotype among the Bartonella-specific serum IgG antibodies. These data indicate that B. henselae induces cell-mediated immune responses with a Th1 phenotype in immunocompetent C57BL/6 mice.
Figures




References
-
- Arvand M, Wendt C, Regnath T, Ullrich R, Hahn H. Characterization of Bartonella henselae isolated from bacillary angiomatosis lesions in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient in Germany. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:1296–1299. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

