Identification of TSIX, encoding an RNA antisense to human XIST, reveals differences from its murine counterpart: implications for X inactivation
- PMID: 11555794
- PMCID: PMC1274371
- DOI: 10.1086/324022
Identification of TSIX, encoding an RNA antisense to human XIST, reveals differences from its murine counterpart: implications for X inactivation
Abstract
X inactivation is the mammalian method for X-chromosome dosage compensation, but some features of this developmental process vary among mammals. Such species variations provide insights into the essential components of the pathway. Tsix encodes a transcript antisense to the murine Xist transcript and is expressed in the mouse embryo only during the initial stages of X inactivation; it has been shown to play a role in imprinted X inactivation in the mouse placenta. We have identified its counterpart within the human X inactivation center (XIC). Human TSIX produces a >30-kb transcript that is expressed only in cells of fetal origin; it is expressed from human XIC transgenes in mouse embryonic stem cells and from human embryoid-body-derived cells, but not from human adult somatic cells. Differences in the structure of human and murine genes indicate that human TSIX was truncated during evolution. These differences could explain the fact that X inactivation is not imprinted in human placenta, and they raise questions about the role of TSIX in random X inactivation.
Figures

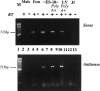

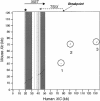
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Celera, http://public.celera.com/index.cfm (for publicly available human genome sequence)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for human XIC reference sequence [accession number U80460] and mouse XIC reference sequences [accession numbers AJ010350, M97167, L04961, U41394, X999460])
-
- GeneBuilder, http://125.itba.mi.cnr.it/~webgene/genebuilder.html (for gene-structure prediction)
-
- HCtata, http://125.itba.mi.cnr.it/~webgene/wwwHC_tata.html (for identification of promoter elements)
-
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory Gene Recognition and Assembly Internet Link, http://compbio.ornl.gov/Grail-1.3/ (Grail, version 1.3, for CpG island identification)
References
-
- Brockdorff N, Ashworth A, Kay G, McCabe V, Norris DP, Cooper P, Swift S, Rastan S (1992) The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell 71:515–526 - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Hendrich BD, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Xing Y, Lawrence J, Willard HF (1992) The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell 71:527–542 - PubMed
-
- Chow JC, Clemson CM, Lawrence JB, Brown CJ (2000) XIST expression in human embryonal carcinoma lines: identification of novel sense and antisense transcripts. Am J Hum Genet Suppl 67:44
-
- Heard E, Clerc P, Avner P (1997) X-chromosome inactivation in mammals. In: Campbell A, Anderson W, Jones EW (eds) Annual review of genetics. Vol 31. Annual Reviews Inc, Palo Alto, California, pp 572–610 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

