Phase i/ii trial of the pharmacokinetics, safety, and antiretroviral activity of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults
- PMID: 11557462
- PMCID: PMC90724
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.10.2733-2739.2001
Phase i/ii trial of the pharmacokinetics, safety, and antiretroviral activity of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults
Abstract
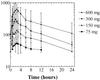
Tenofovir DF is an antiviral nucleotide with activity against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). The pharmacokinetics, safety, and activity of oral tenofovir DF in HIV-1-infected adults were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, escalating-dose study of four doses (75, 150, 300, and 600 mg given once daily). Subjects received a single dose of tenofovir DF or a placebo, followed by a 7-day washout period. Thereafter, subjects received their assigned study drug once daily for 28 days. Pharmacokinetic parameters were dose proportional and demonstrated no change with repeated dosing. Reductions in plasma HIV-1 RNA were dose related at tenofovir DF doses of 75 to 300 mg, but there was no increase in virus suppression between the 300- and 600-mg dose cohorts, despite dose-proportional increases in drug exposure. Grade III or IV adverse events were limited to laboratory abnormalities, including elevated creatine phosphokinase and liver function tests, which resolved with or without drug discontinuation and without sequelae. No patients developed detectable sequence changes in the reverse transcriptase gene.
Figures

References
-
- Anonymous. Division of AIDS table for grading severity of adverse experiences. Rockville, Md: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; 1996.
-
- Arimilli M, Kim C, Bischofberger N, Dougherty J, Mulato A, Oliyai R, Shaw J P, Cundy K C, Bischofberger N. Synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation and oral bioavailability of prodrugs of the antiretroviral agent 9-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)-propyl]adenine (PMA) Antiviral Chem Chemother. 1997;8:557–564.
-
- Deeks S G, Barditch-Crovo P, Lietman P S, Hwang F, Cundy K C, Rooney J F, Hellmann N S, Safrin S, Kahn J O. The safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiretroviral activity of intravenous 9-[2-(R)-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]adenine, a novel anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) therapy, in HIV-infected adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:2380–2384. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deeks S G, Collier A, Lalezari J, Pavia A, Rodrigue D, Drew W L, Toole J, Jaffe H, Mulato A S, Lamy P D, Li W, Cherrington J M, Hillmann N, Kahn J. The safety and efficacy of adefovir dipivoxil, a novel anti-HIV therapy, in HIV infected adults. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1517–1523. - PubMed
-
- Miller M D, Anton K E, Mulato A S, Lamy P D, Cherrington J M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expressing the lamivudine-associated M184V mutation in reverse transcriptase shows increased susceptibility to adefovir and decreased replication capacity in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:92–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

