Treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide: two year follow up of a double blind, placebo controlled trial versus sulfasalazine
- PMID: 11557646
- PMCID: PMC1753377
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.60.10.913
Treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide: two year follow up of a double blind, placebo controlled trial versus sulfasalazine
Abstract
Objective: Recent studies have demonstrated the short term efficacy of leflunomide. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of leflunomide and sulfasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis over a two year follow up period.
Methods: 358 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a double blind trial were randomly allocated to receive either leflunomide 20 mg/day, placebo, or sulfasalazine 2 g/day. Those completing six months of treatment (n=230) were given the option to continue in 12 (n=168) and 24 (n=146) month double blinded extensions; the placebo group switched to sulfasalazine. This report compares efficacy and safety of leflunomide with sulfasalazine in the 6, 12, and 24 month patient cohorts.
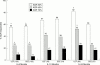
Results: The efficacy seen at six months was maintained at 12 and 24 months. Twenty four month cohorts on leflunomide showed significant improvement compared with sulfasalazine in doctor (-1.46 v -1.11, p=0.03) and patient (-1.61 v -1.04, p<0.001) global assessments, ACR20% response (82% v 60%, p<0.01), and functional ability (Deltamean HAQ -0.65 v -0.36, p=0.0149; DeltaHAQ disability index -0.89 v -0.60, p=0.059). Improvement in other variables was comparable for the two drugs, including slowing of disease progression. Improved HAQ scores in 6, 12, and 24 month leflunomide cohorts were seen in both non-responders (24%, 29%, 35%, respectively v sulfasalazine 8%, 10%, 27%) and ACR20% responders (leflunomide 63%, 62%, 66% v sulfasalazine 50%, 64%, 44%). Leflunomide is well tolerated at doses of 20 mg. No unexpected adverse events or late toxicity were noted during the two year period. Diarrhoea, nausea, and alopecia were less frequent with continued treatment.
Conclusion: These long term data confirm that leflunomide is an efficacious and safe disease modifying antirheumatic drug.
Figures





Comment in
-
Leflunomide decreases joint erosions and induces reparative changes in a patient with psoriatic arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Oct;61(10):942-3. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.10.942. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002. PMID: 12228172 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

