Decreased diffusion in central pontine myelinolysis
- PMID: 11559493
- PMCID: PMC7974564
Decreased diffusion in central pontine myelinolysis
Abstract
Two patients with central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) were studied with diffusion-weighted MR imaging 1 week after onset of tetraplegia. In both patients, affected white matter showed hyperintensity on diffusion-weighted images associated with a decrease in apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values. In one patient studied serially, ADC values normalized by 3 weeks after tetraplegia. Early in the clinical course, diagnosis of CPM can sometimes be difficult. Hyperintensity on diffusion-weighted images may therefore have diagnostic utility. Decreased lesional ADC values support the notion that CPM is a consequence of relative intracellular hypotonicity.
Figures
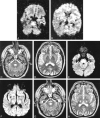
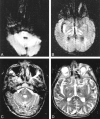
References
-
- Adams RA, Victor M, Mancall EL. Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholics and malnourished patients. Arch Neurol Psychiat 1959;81:154-172 - PubMed
-
- McKee AC, Winkelman MD, Banker BQ. Central pontine myelinolysis in severely burned patients: relationship to serum hyperosmolality [published erratum appears in Neurology 1988;38:1662]. Neurology 1988;38:1211-1217 - PubMed
-
- Karp BI, Laureno R. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: a neurologic disorder following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Medicine (Baltimore) 1993;72:359-373 - PubMed
-
- Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000;217:331-345 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
