Engraftment of NOD/SCID mice with human CD34(+) cells transduced by concentrated oncoretroviral vector particles pseudotyped with the feline endogenous retrovirus (RD114) envelope protein
- PMID: 11559834
- PMCID: PMC114573
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.20.9995-9999.2001
Engraftment of NOD/SCID mice with human CD34(+) cells transduced by concentrated oncoretroviral vector particles pseudotyped with the feline endogenous retrovirus (RD114) envelope protein
Abstract
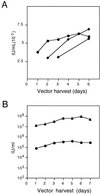
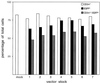
Oncoretrovirus vectors pseudotyped with the feline endogenous retrovirus (RD114) envelope protein produced by the FLYRD18 packaging cell line have previously been shown to transduce human hematopoietic progenitor cells with a greater efficiency than similar amphotropic envelope-pseudotyped vectors. In this report, we describe the production and efficient concentration of RD114-pseudotyped murine leukemia virus (MLV)-based vectors. Following a single round of centrifugation, vector supernatants were concentrated approximately 200-fold with a 50 to 70% yield. Concentrated vector stocks transduced prestimulated human CD34(+) (hCD34(+)) cells with approximately 69% efficiency (n = 7, standard deviation = 4.4%) using a single addition of vector at a low multiplicity of infection (MOI = 5). Introduction of transduced hCD34(+) cells into irradiated NOD/SCID recipients resulted in multilineage engraftment with long-term transgene expression. These data demonstrate that RD114-pseudotyped MLV-based vectors can be efficiently concentrated to high titers and that hCD34(+) cells transduced with concentrated vector stocks retain in vivo repopulating potential. These results highlight the potential of RD114-pseudotyped oncoretrovirus vectors for future clinical implementation in hematopoietic stem cell gene transfer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transduction of human hematopoietic stem cells by lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with the RD114-TR chimeric envelope glycoprotein.Hum Gene Ther. 2007 Sep;18(9):811-20. doi: 10.1089/hum.2006.138. Hum Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17824830
-
Gene transfer to repopulating human CD34+ cells using amphotropic-, GALV-, or RD114-pseudotyped HIV-1-based vectors from stable producer cells.Mol Ther. 2005 Mar;11(3):452-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.10.014. Mol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15727942
-
RD114-pseudotyped oncoretroviral vectors. Biological and physical properties.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;938:262-76; discussion 276-7. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458516
-
Preparation of pseudotyped retroviral vector.Methods Mol Med. 2002;69:149-59. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-141-8:149. Methods Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 11987774 Review. No abstract available.
-
Lentiviral gene delivery to plasmolipin-expressing cells using Mus caroli endogenous retrovirus envelope protein.Biochimie. 2017 Nov;142:226-233. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28912093 Review.
Cited by
-
Jun blockade of erythropoiesis: role for repression of GATA-1 by HERP2.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(17):7779-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7779-7794.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15314183 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized transduction of canine paediatric CD34(+) cells using an MSCV-based bicistronic vector.Vet Res Commun. 2006 Nov;30(8):881-901. doi: 10.1007/s11259-006-3356-7. Vet Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 17139538
-
Evaluation of different protocols for gene transfer into non-obese diabetes/severe combined immunodeficiency disease mouse repopulating cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007 Mar;133(3):199-209. doi: 10.1007/s00432-006-0158-9. Epub 2006 Oct 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17053889 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient clinical-grade γ-retroviral vector purification by high-speed centrifugation for CAR T cell manufacturing.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022 Dec 9;28:116-128. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.12.006. eCollection 2023 Mar 9. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2022. PMID: 36620071 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo gene transfer using a nonprimate lentiviral vector pseudotyped with Ross River Virus glycoproteins.J Virol. 2002 Sep;76(18):9378-88. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9378-9388.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12186920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allay J A, Persons D A, Galipeau J, Riberdy J M, Ashmun R A, Blakley R L, Sorrentino B P. In vivo selection of retrovirally transduced hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med. 1998;4:1136–1143. - PubMed
-
- Barquinero J, Segovia J C, Ramirez M, Limon A, Guenechea G, Puig T, Briones J, Garcia J, Bueren J A. Efficient transduction of human hematopoietic repopulating cells generating stable engraftment of transgene-expressing cells in NOD/SCID mice. Blood. 2000;95:3085–3093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

