Isolation and characterization of dermal lymphatic and blood endothelial cells reveal stable and functionally specialized cell lineages
- PMID: 11560995
- PMCID: PMC2195953
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.194.6.797
Isolation and characterization of dermal lymphatic and blood endothelial cells reveal stable and functionally specialized cell lineages
Abstract
A plexus of lymphatic vessels guides interstitial fluid, passenger leukocytes, and tumor cells toward regional lymph nodes. Microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) of lymph channels (LECs) are difficult to distinguish from those of blood vessels (BECs) because both express a similar set of markers, such as CD31, CD34, podocalyxin, von Willebrand factor (vWF), etc. Analysis of the specific properties of LECs was hampered so far by lack of tools to isolate LECs. Recently, the 38-kD mucoprotein podoplanin was found to be expressed by microvascular LECs but not BECs in vivo. Here we isolated for the first time podoplanin(+) LECs and podoplanin(-) BECs from dermal cell suspensions by multicolor flow cytometry. Both EC types were propagated and stably expressed VE-cadherin, CD31, and vWF. Molecules selectively displayed by LECs in vivo, i.e., podoplanin, the hyaluronate receptor LYVE-1, and the vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF)-C receptor, fms-like tyrosine kinase 4 (Flt-4)/VEGFR-3, were strongly expressed by expanded LECs, but not BECs. Conversely, BECs but not LECs expressed VEGF-C. LECs as well as BECs formed junctional contacts with similar molecular composition and ultrastructural features. Nevertheless, the two EC types assembled in vitro in vascular tubes in a strictly homotypic fashion. This EC specialization extends to the secretion of biologically relevant chemotactic factors: LECs, but not BECs, constitutively secrete the CC chemokine receptor (CCR)7 ligand secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine (SLC)/CCL21 at their basal side, while both subsets, upon activation, release macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-3alpha/CCL20 apically. These results demonstrate that LECs and BECs constitute stable and specialized EC lineages equipped with the potential to navigate leukocytes and, perhaps also, tumor cells into and out of the tissues.
Figures
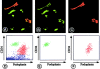
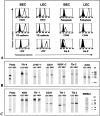




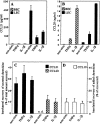
Comment in
-
Lymphatic vessels as targets of tumor therapy?J Exp Med. 2001 Sep 17;194(6):F37-42. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.f37. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11561002 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Skobe M., Detmar M. Structure, function, and molecular control of the skin lymphatic system. J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2000;5:14–19. - PubMed
-
- Witte M.H., Way D.L., Witte C.L., Bernas M. Lymphangiogenesismechanisms, significance, and clinical implication. EXS. 1997;79:65–112. - PubMed
-
- Ryan T.J. Structure and function of lymphatics J. Invest. Dermatol. 93Suppl.1989. 18S 24S - PubMed
-
- Breiteneder-Geleff S., Soleiman A., Kowalski H., Horvat R., Amann G., Kriehuber E., Diem K., Weninger W., Tschachler E., Alitalo K., Kerjaschki D. Angiosarcomas express mixed endothelial phenotypes of blood and lymphatic capillariespodoplanin as a specific marker for lymphatic endothelium. Am. J. Pathol. 1999;154:385–394. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jaksits S., Kriehuber E., Charbonnier A.-S., Rappersberger K., Stingl G., Maurer D. CD34+ cell-derived CD14+ precursor cells develop into Langerhans cells in a TGF-beta 1-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 1999;163:4869–4877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

