Bupivacaine effects on hKv1.5 channels are dependent on extracellular pH
- PMID: 11564654
- PMCID: PMC1572951
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704251
Bupivacaine effects on hKv1.5 channels are dependent on extracellular pH
Abstract
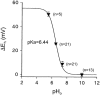
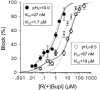
1. Bupivacaine-induced cardiotoxicity increases in hypoxic and acidotic conditions. We have analysed the effects of R(+)bupivacaine on hKv1.5 channels stably expressed in Ltk(-) cells using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique, at three different extracellular pH (pH(o)), 6.5, 7.4 and 10.0. 2. Acidification of the pH(o) from 7.4 to 6.5 decreased 4 fold the potency of R(+)bupivacaine to block hKv1.5 channels. At pH(o) 10.0, the potency of the drug increased approximately 2.5 fold. 3. Block induced by R(+)bupivacaine at pH(o) 6.5, 7.4 and 10.0, was voltage- and time-dependent in a manner consistent with an open state block of hKv1.5 channels. 4. At pH(o) 6.5, but not at pH(o) 7.4 or 10.0, R(+)bupivacaine increased by 95+/-3 % (n=6; P<0.05) the hKv1.5 current recorded at -10 mV, likely due to a drug-induced shift of the midpoint of activation (DeltaV=-8.5+/-1.4 mV; n=7). 5. R(+)bupivacaine development of block exhibited an 'instantaneous' component of block at the beginning of the depolarizing pulse, which averaged 12.5+/-1.8% (n=5) and 4.6+/-1.6% (n=6), at pH(o) 6.5 and 7.4, respectively, and that was not observed at pH(o) 10.0. 6. It is concluded that: (a) alkalinization of the pH(o) increases the potency of block of R(+)bupivacaine, and (b) at pH(o) 6.5, R(+)bupivacaine induces an 'agonist effect' of hKv1.5 current when recorded at negative membrane potentials.
Figures


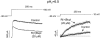

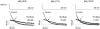
Similar articles
-
Stereoselective effects of the enantiomers of a new local anaesthetic, IQB-9302, on a human cardiac potassium channel (Kv1.5).Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jan;132(2):385-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703844. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11159686 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective block of a human cardiac potassium channel (Kv1.5) by bupivacaine enantiomers.Biophys J. 1995 Aug;69(2):418-27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79914-3. Biophys J. 1995. PMID: 8527655 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a quaternary bupivacaine derivative on delayed rectifier K(+) currents.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 May;130(2):391-401. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703334. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10807678 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of potency and stereoselective block of hKv1.5 channels induced by local anesthetics.Mol Pharmacol. 1998 Jul;54(1):162-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.54.1.162. Mol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9658202
-
Effects of bupivacaine and a novel local anesthetic, IQB-9302, on human cardiac K+ channels.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Feb;296(2):573-83. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11160646
Cited by
-
Enhancement of delayed-rectifier potassium conductance by low concentrations of local anaesthetics in spinal sensory neurones.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jun;136(4):540-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704754. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12055132 Free PMC article.
-
PKC inhibition results in a Kv 1.5 + Kv β1.3 pharmacology closer to Kv 1.5 channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;171(21):4914-26. doi: 10.1111/bph.12822. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24946104 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of the Dissociation Rate in Ion Channel Blocking.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Feb 9;12:33. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00033. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29479308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ÅBERG G. Toxicological and local anaesthetic effects of optically active isomers of two local anaesthetic compounds. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1972;31:273–286. - PubMed
-
- BETHELL H.W., VANDENBERG J.I., SMITH G.A., GRACE A.A. Changes in ventricular repolarization during acidosis and low- flow ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;275:H551–H561. - PubMed
-
- BUSCH A.E., HURST R.S., NORTH R.A., ADELMAN J.P., KAVANAUGH M.P. Current inactivation involves a histidine residue in the pore of the rat lymphocyte potassium channel RGK5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1991;179:1384–1390. - PubMed

