Hydrogen peroxide-mediated inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inhibitory kappa B kinase activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 11564658
- PMCID: PMC1572956
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704259
Hydrogen peroxide-mediated inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inhibitory kappa B kinase activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells
Abstract
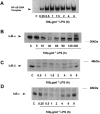
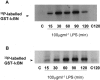
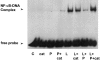
1. In rat aortic smooth muscle cells (RASMC), exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) resulted in NF-kappaB-DNA binding, degradation of IkappaB-alpha, -beta and -epsilon and increased activity of both alpha and beta isoforms of inhibitory kappa B kinase (IKK). 2. Expression of dominant-negative (DN)-IKK-alpha, IKK-beta and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) abolished LPS-stimulated NF-kappaB reporter activity, suggesting that activation of a NIK/IKK-dependent pathway is indispensable for NF-kappaB activation by LPS in this cell type. 3. The tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor, pervanadate, abolished LPS-stimulated NF-kappaB-DNA-binding activity. However, the effect of pervanadate was shown to be mediated by excess hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) present in the reaction mix. Preincubation of RASMC with H(2)O(2) inhibited LPS-stimulated IKK kinase activity and downstream NF-kappaB-DNA binding activity. 4. H(2)O(2) also strongly stimulated p38 MAP kinase activity in RASMCs. Effective inhibition of this pathway using SB203580 did not reverse the effects of H(2)O(2) on LPS-stimulated IKK/NF-kappaB signalling. 5. These studies show that hydrogen peroxide-mediated inhibition of LPS-stimulated NF-kappaB activation in RASMC occurs upstream of IKK. The inhibitory effect of H(2)O(2) is not due to tyrosine phosphatase inhibition, it is mediated by H(2)O(2) through a mechanism which is independent of any cross-talk involving MAP kinase homologues.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated JNK activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells by pharmacological and adenovirus-mediated inhibition of inhibitory kappa B kinase signalling.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul;139(5):1041-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705330. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12839879 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells: possible involvement of the NIK-IKK, ERK1/2, p38 and JNK pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug 7;542(1-3):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.044. Epub 2006 May 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16797002
-
Dipyridamole activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 mediates inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Jul 17;541(3):138-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.05.002. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16765938
-
The effect of reactive oxygen species on the synthesis of prostanoids from arachidonic acid.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;64(4):409-21. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24101387 Review.
-
Ubiquitin signalling in the NF-kappaB pathway.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;7(8):758-65. doi: 10.1038/ncb0805-758. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16056267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of SCF beta-TrCP-dependent I kappaB alpha ubiquitination by hydrogen peroxide.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2665-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.060822. Epub 2009 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19933270 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated JNK activity in rat aortic smooth muscle cells by pharmacological and adenovirus-mediated inhibition of inhibitory kappa B kinase signalling.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul;139(5):1041-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705330. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12839879 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of inhibitory kappa B kinase-beta abrogates induction of nitric oxide synthase in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat aortic smooth muscle cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Sep;146(2):217-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706308. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15997236 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of pacemaker activity in interstitial cells of Cajal by LPS via NF-κB and MAP kinase.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1210-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1210. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482668 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Differentially Regulate Bone Turnover in an Age-Specific Manner in Catalase Transgenic Female Mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Jul;358(1):50-60. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.233213. Epub 2016 May 12. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 27189961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ABE J., OKUDA M., HUANG Q., YOSHIZUMI M., BERK B.C. Reactive oxygen species activate p90 ribosomal S6 kinase via Fyn and Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:1739–1748. - PubMed
-
- ALPERT D., SCHWENGER P., HAN J., VILCEK J. Cell stress and MKK6b-mediated p38 MAP kinase activation inhibit tumor necrosis factor-induced IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:22176–22183. - PubMed
-
- ARUOMA O.I., HALLIWELL B., HOEY B.M., BUTLER J. The antioxidant action of N-acetylcysteine: its reaction with hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, superoxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1989;6:593–597. - PubMed
-
- BAE G.-U., SEO D.-W., KWON H.-K., LEE H.Y., HONG S., LEE Z.-W., HA K.-S., LEE H.-W., HAN J.-W. Hydrogen peroxide activates p70(S6k) signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:32596–32602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

