Eg5 is static in bipolar spindles relative to tubulin: evidence for a static spindle matrix
- PMID: 11564753
- PMCID: PMC2150813
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200106011
Eg5 is static in bipolar spindles relative to tubulin: evidence for a static spindle matrix
Abstract
We used fluorescent speckle microscopy to probe the dynamics of the mitotic kinesin Eg5 in Xenopus extract spindles, and compared them to microtubule dynamics. We found significant populations of Eg5 that were static over several seconds while microtubules flux towards spindle poles. Eg5 dynamics are frozen by adenylimidodiphosphate. Bulk turnover experiments showed that Eg5 can exchange between the spindle and the extract with a half life of <55 s. Eg5 distribution in spindles was not perturbed by inhibition of its motor activity with monastrol, but was perturbed by inhibition of dynactin with p50 dynamitin. We interpret these data as revealing the existence of a static spindle matrix that promotes Eg5 targeting to spindles, and transient immobilization of Eg5 within spindles. We discuss alternative interpretations of the Eg5 dynamics we observe, ideas for the biochemical nature of a spindle matrix, and implications for Eg5 function.
Figures

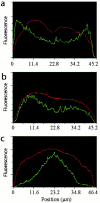
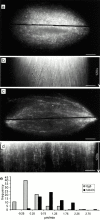



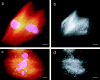
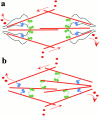
Comment in
-
Searching for a spindle matrix.J Cell Biol. 2001 Sep 17;154(6):1102-4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108139. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11564751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blangy, A., H.A. Lane, P. d'Herin, M. Harper, M. Kress, and E.A. Nigg. 1995. Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin-related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell. 83:1159–1169. - PubMed
-
- Blangy, A., L. Arnaud, and E.A. Nigg. 1997. Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 protein kinase regulates binding of the kinesin-related motor HsEg5 to the dynactin subunit p150. J. Biol. Chem. 272:19418–19424. - PubMed
-
- Desai, A., A. Murray, T.J. Mitchison, and C.E. Walczak. 1999. The use of Xenopus egg extracts to study mitotic spindle assembly and function in vitro. Methods Cell Biol. 61:385–412. - PubMed
-
- Dionne, M.A., L. Howard, and D.A. Compton. 1999. NuMA is a component of an insoluble matrix at mitotic spindle poles. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. 42:189–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

