The xeroderma pigmentosum group E gene product DDB2 is a specific target of cullin 4A in mammalian cells
- PMID: 11564859
- PMCID: PMC99852
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6738-6747.2001
The xeroderma pigmentosum group E gene product DDB2 is a specific target of cullin 4A in mammalian cells
Abstract
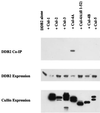
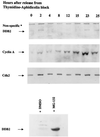
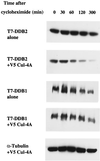
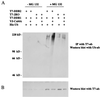
The damaged-DNA binding protein DDB consists of two subunits, DDB1 (127 kDa) and DDB2 (48 kDa). Mutations in the DDB2 subunit have been detected in patients suffering from the repair deficiency disease xeroderma pigmentosum (group E). In addition, recent studies suggested a role for DDB2 in global genomic repair. DDB2 also exhibits transcriptional activity. We showed that expression of DDB1 and DDB2 stimulated the activity of the cell cycle regulatory transcription factor E2F1. Here we show that DDB2 is a cell cycle-regulated protein. It is present at a low level in growth-arrested primary fibroblasts, and after release the level peaks at the G(1)/S boundary. The cell cycle regulation of DDB2 involves posttranscriptional mechanisms. Moreover, we find that an inhibitor of 26S proteasome increases the level of DDB2, suggesting that it is regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Our previous study indicated that the cullin family protein Cul-4A associates with the DDB2 subunit. Because cullins are involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, we investigated the role of Cul-4A in regulating DDB2. Here we show that DDB2 is a specific target of Cul-4A. Coexpression of Cul-4A, but not Cul-1 or other highly related cullins, increases the ubiquitination and the decay rate of DDB2. A naturally occurring mutant of DDB2 (2RO), which does not bind Cul-4A, is not affected by coexpression of Cul-4A. Studies presented here identify a specific function of the Cul-4A gene, which is amplified and overexpressed in breast cancers.
Figures



References
-
- Abramic M, Levine A S, Protic M. Purification of an ultraviolet-inducible, damage-specific DNA-binding protein from primate cells. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:22439–22500. - PubMed
-
- Bai C, Sen P, Mathias N, Hofmann K, Goebl M, Harper J W, Elledge S J. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulation to ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Chen L-C, Manjeshwar S, Lu Y, Moore D, Ljung B-M, Kuo W-L, Dairkee S H, Wernick M, Colins C, Smith H S. The human homologue for the Caenorhabditis elegans Cul-4 gene is amplified and overexpressed in primary breast cancers. Cancer Res. 1998;58:3677–3683. - PubMed
-
- Cho R J, Huang M, Campbell M J, Dong H, Steinmetz L, Sapinoso L, Hampton G, Elledge S J, Davis R W, Lockhart D J. Transcriptional regulation and function during the human cell cycle. Nat Genet. 2001;27:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Chu G, Chang E. Xeroderma pigmentosum group E cells lack a nuclear factor that binds to damaged DNA. Science. 1988;242:564–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
