Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 assembles a novel signaling complex containing protein phosphatase 1 and inhibitor 1
- PMID: 11564868
- PMCID: PMC99861
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6841-6850.2001
Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 assembles a novel signaling complex containing protein phosphatase 1 and inhibitor 1
Abstract
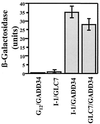
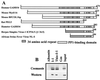
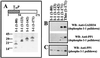
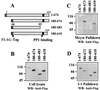
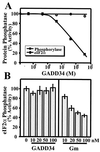
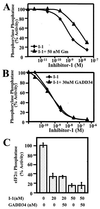
The growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein, GADD34, was identified by its interaction with human inhibitor 1 (I-1), a protein kinase A (PKA)-activated inhibitor of type 1 protein serine/threonine phosphatase (PP1), in a yeast two-hybrid screen of a human brain cDNA library. Recombinant GADD34 (amino acids 233 to 674) bound both PKA-phosphorylated and unphosphorylated I-1(1-171). Serial truncations mapped the C terminus of I-1 (amino acids 142 to 171) as essential for GADD34 binding. In contrast, PKA phosphorylation was required for PP1 binding and inhibition by the N-terminal I-1(1-80) fragment. Pulldowns of GADD34 proteins expressed in HEK293T cells showed that I-1 bound the central domain of GADD34 (amino acids 180 to 483). By comparison, affinity isolation of cellular GADD34/PP1 complexes showed that PP1 bound near the C terminus of GADD34 (amino acids 483 to 619), a region that shows sequence homology with the virulence factors ICP34.5 of herpes simplex virus and NL-S of avian sarcoma virus. While GADD34 inhibited PP1-catalyzed dephosphorylation of phosphorylase a, the GADD34-bound PP1 was an active eIF-2alpha phosphatase. In brain extracts from active ground squirrels, GADD34 bound both I-1 and PP1 and eIF-2alpha was largely dephosphorylated. In contrast, the I-1/GADD34 and PP1/GADD34 interactions were disrupted in brain from hibernating animals, in which eIF-2alpha was highly phosphorylated at serine-51 and protein synthesis was inhibited. These studies suggested that modification of the I-1/GADD34/PP1 signaling complex regulates the initiation of protein translation in mammalian tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Aggen J B, Nairn A C, Chamberlin R. Regulation of protein phosphatase-1. Chem Biol. 2000;7:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Bibb J A, Nishi A, O'Callaghan J P, Ule J, Lan M, Snyder G L, Horiuchi A, Saito T, Hisanaga S, Czernik A J, Nairn A C, Greengard P. Phosphorylation of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 by Cdk5 J. Biol Chem. 2001;276:14490–14497. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer R D, Connor J H, Brown G P, Wong T, Shenolikar S, Iyengar R, Landau E M. Gating of CaMKII by cAMP-regulated protein phosphatase activity during LTP. Science. 1998;280:1940–1942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
