Gene targeting of envoplakin, a cytoskeletal linker protein and precursor of the epidermal cornified envelope
- PMID: 11564887
- PMCID: PMC99880
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.7047-7053.2001
Gene targeting of envoplakin, a cytoskeletal linker protein and precursor of the epidermal cornified envelope
Abstract
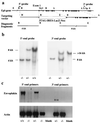
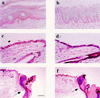
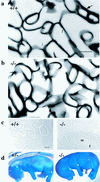
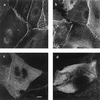
Envoplakin, a member of the plakin family of cytoskeletal linker proteins, is localized in desmosomes of stratified epithelial cells and is a component of the epidermal cornified envelope. Gene targeting in mouse embryonic stem cells was used to generate a null allele of envoplakin. No envoplakin transcripts from the targeted allele could be detected in the skin of newborn mice. Mice homozygous for the targeted allele were born in the normal Mendelian ratio and were fertile. They did not develop any discernible pathological phenotype up to the age of 1 year. The ultrastructural appearance of cornified envelopes from adult epidermis was indistinguishable between wild-type and knockout mice, and there was no evidence that the absence of envoplakin affected the subcellular distribution of periplakin or desmoplakin, two other plakins found in desmosomes. The proportion of immature cornified envelopes in the epidermis of newborn mice was greater in envoplakin-null animals than in heterozygous littermates or wild-type mice, and the envelopes had a larger surface area. This correlated with a slight delay in barrier acquisition during embryonic development. We conclude that although envoplakin is part of the scaffolding on which the cornified envelope is assembled, it is not essential for envelope formation or epidermal barrier function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Periplakin gene targeting reveals a constituent of the cornified cell envelope dispensable for normal mouse development.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(14):6410-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.14.6410-6418.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15226441 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular distribution of envoplakin and periplakin: insights into their role as precursors of the epidermal cornified envelope.J Cell Biol. 2000 Oct 30;151(3):573-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.573. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11062259 Free PMC article.
-
Periplakin, a novel component of cornified envelopes and desmosomes that belongs to the plakin family and forms complexes with envoplakin.J Cell Biol. 1997 Dec 29;139(7):1835-49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.7.1835. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9412476 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Analysis of Periplakin and Envoplakin, Cytoskeletal Linkers, and Cornified Envelope Precursor Proteins.Methods Enzymol. 2016;569:309-29. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 26778565 Review.
-
Epithelial structural proteins of the skin and oral cavity: function in health and disease.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2000;11(4):383-408. doi: 10.1177/10454411000110040101. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2000. PMID: 11132762 Review.
Cited by
-
Periplakin gene targeting reveals a constituent of the cornified cell envelope dispensable for normal mouse development.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(14):6410-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.14.6410-6418.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15226441 Free PMC article.
-
A mouse model of harlequin ichthyosis delineates a key role for Abca12 in lipid homeostasis.PLoS Genet. 2008 Sep 19;4(9):e1000192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000192. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18802465 Free PMC article.
-
Mice deficient in involucrin, envoplakin, and periplakin have a defective epidermal barrier.J Cell Biol. 2007 Dec 31;179(7):1599-612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200706187. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18166659 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal barrier defects link atopic dermatitis with altered skin cancer susceptibility.Elife. 2014 May 5;3:e01888. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01888. Elife. 2014. PMID: 24843010 Free PMC article.
-
Amniotic fluid activates the nrf2/keap1 pathway to repair an epidermal barrier defect in utero.Dev Cell. 2012 Dec 11;23(6):1238-46. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.11.002. Dev Cell. 2012. PMID: 23237955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aho S, McLean W H, Li K, Uitto J. cDNA cloning, mRNA expression and chromosomal mapping of human and mouse periplakin genes. Genomics. 1998;48:242–247. - PubMed
-
- Denzel A, Otto F, Girod A, Pepperkok R, Watson R, Rosewell I, Bergeron J J M, Solari R C E, Owen M J. The p24 family member p23 is required for early embryonic development. Curr Biol. 1999;10:55–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
