Independent function of two destruction domains in hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha chains activated by prolyl hydroxylation
- PMID: 11566883
- PMCID: PMC125617
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.18.5197
Independent function of two destruction domains in hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha chains activated by prolyl hydroxylation
Abstract
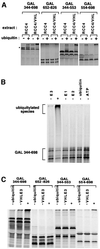
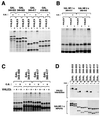
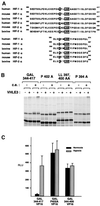
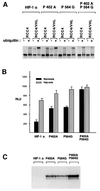
Oxygen-dependent proteolytic destruction of hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha (HIF-alpha) subunits plays a central role in regulating transcriptional responses to hypoxia. Recent studies have defined a key function for the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor E3 ubiquitin ligase (VHLE3) in this process, and have defined an interaction with HIF-1 alpha that is regulated by prolyl hydroxylation. Here we show that two independent regions within the HIF-alpha oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODDD) are targeted for ubiquitylation by VHLE3 in a manner dependent upon prolyl hydroxylation. In a series of in vitro and in vivo assays, we demonstrate the independent and non-redundant operation of each site in regulation of the HIF system. Both sites contain a common core motif, but differ both in overall sequence and in the conditions under which they bind to the VHLE3 ligase complex. The definition of two independent destruction domains implicates a more complex system of pVHL-HIF-alpha interactions, but reinforces the role of prolyl hydroxylation as an oxygen-dependent destruction signal.
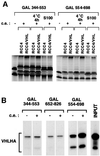
Figures


References
-
- Berra E., Milanini,J., Richard,D.E., LeGall,M., Vinals,F., Gothie,E., Roux,D., Pages,G. and Pouyssegur,J. (2000) Signaling angiogenesis via p42/p44 MAP kinase and hypoxia. Biochem. Pharmacol., 60, 1171–1178. - PubMed
-
- Cockman M.E. et al. (2000) Hypoxia inducible factor-α binding and ubiquitylation by the von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 25733–25741. - PubMed
-
- Ema M., Hirota,K., Mimura,J., Abe,H., Yodoi,J., Sogawa,K., Poellinger,L. and Fujii-Kuriyama,Y. (1999) Molecular mechanisms of transcription activation by HLF and HIF1α in response to hypoxia: their stabilization and redox signal-induced interaction with CBP/p300. EMBO J., 18, 1905–1914. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang L.E., Arany,Z., Livingston,D.M. and Bunn,H.F. (1996) Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily on redox-sensitive stabilization of its α subunit. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 32253–32259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

