Delayed inner ear maturation and neuronal loss in postnatal Igf-1-deficient mice
- PMID: 11567053
- PMCID: PMC6762913
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-19-07630.2001
Delayed inner ear maturation and neuronal loss in postnatal Igf-1-deficient mice
Abstract
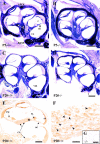
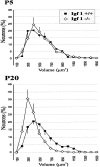
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) has been shown to play a key role during embryonic and postnatal development of the CNS, but its effect on a sensory organ has not been studied in vivo. Therefore, we examined cochlear growth, differentiation, and maturation in Igf-1 gene knock-out mice at postnatal days 5 (P5), P8, and P20 by using stereological methods and immunohistochemistry. Mutant mice showed reduction in size of the cochlea and cochlear ganglion. An immature tectorial membrane and a significant decrease in the number and size of auditory neurons were also evident at P20. IGF-1-deficient cochlear neurons showed increased caspase-3-mediated apoptosis, along with aberrant expression of the early neural markers nestin and Islet 1/2. Cochlear ganglion and fibers innervating the sensory cells of the organ of Corti presented decreased levels of neurofilament and myelin P(0) in P20 mouse mutants. In addition, an abnormal synaptophysin expression in the somata of cochlear ganglion neurons and sensory hair cells suggested the persistence of an immature pattern of synapses distribution in the organ of Corti of these animals. These results demonstrate that lack of IGF-1 in mice severely affects postnatal survival, differentiation, and maturation of the cochlear ganglion cells and causes abnormal innervation of the sensory cells in the organ of Corti.
Figures





References
-
- Avendaño C, Dykes RW. Quantitative analysis of anatomical changes in the cuneate nucleus following forelimb denervation: a stereological morphometric study in adult cats. J Comp Neurol. 1996;370:491–500. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Hardy MP, Zhou J, Bondy C, Lupu F, Bellve AR, Efstratiadis A. Effects of an Igf1 gene null mutation on mouse reproduction. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10:903–918. - PubMed
-
- Beck KD, Powell-Braxton L, Widmer HR, Valverde J, Hefti F. Igf1 gene disruption results in reduced brain size, CNS hypomyelination, and loss of hippocampal granule and striatal parvalbumin-containing neurons. Neuron. 1995;14:717–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
