Infantile Alexander disease: spectrum of GFAP mutations and genotype-phenotype correlation
- PMID: 11567214
- PMCID: PMC1274357
- DOI: 10.1086/323799
Infantile Alexander disease: spectrum of GFAP mutations and genotype-phenotype correlation
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet 2001 Dec;69(6):1413
Abstract
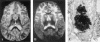
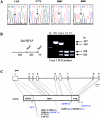
Heterozygous, de novo mutations in the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) gene have recently been reported in 12 patients affected by neuropathologically proved Alexander disease. We searched for GFAP mutations in a series of patients who had heterogeneous clinical symptoms but were candidates for Alexander disease on the basis of suggestive neuroimaging abnormalities. Missense, heterozygous, de novo GFAP mutations were found in exons 1 or 4 for 14 of the 15 patients analyzed, including patients without macrocephaly. Nine patients carried arginine mutations (four had R79H; four had R239C; and one had R239H) that have been described elsewhere, whereas the other five had one of four novel mutations, of which two affect arginine (2R88C and 1R88S) and two affect nonarginine residues (1L76F and 1N77Y). All mutations were located in the rod domain of GFAP, and there is a correlation between clinical severity and the affected amino acid. These results confirm that GFAP mutations are a reliable molecular marker for the diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease, and they also form a basis for the recommendation of GFAP analysis for prenatal diagnosis to detect potential cases of germinal mosaicism.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for Alexander disease [MIM 203450], GFAP [MIM 137780], and keratin 9 [MIM 144200] )
References
-
- Alexander WS (1949) Progressive fibrinoid degeneration of fibrillary astrocytes associated with mental retardation in a hydrocephalic infant. Brain 72:373–381 - PubMed
-
- Bonifas JM, Matsumura K, Chen MA, Berth-Jones J, Hutchison PE, Zloczower M, Fritsch PO, Epstein EH Jr (1994) Mutations of keratin 9 in two families with palmoplantar epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. J Invest Dermatol 103:474–477 - PubMed
-
- Borrett D, Becker LE (1985) Alexander’s disease, a disease of astrocytes. Brain 108:367–385 - PubMed
-
- Brenner M, Johnson AB, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Rodriguez D, Goldman JE, Messing A (2001) Mutations in GFAP, encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein, are associated with Alexander disease. Nature Genet 27:117–120 - PubMed
-
- Brenner M, Lampel K, Nakatani Y, Mill J, Banner C, Mearow K, Dohadwala M, Lipsky R, Freese E (1990) Characterization of human cDNA and genomic clones for glial fibrillary acidic protein. Mol Brain Res 7:277–286 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

