Niemann-Pick disease type C: spectrum of HE1 mutations and genotype/phenotype correlations in the NPC2 group
- PMID: 11567215
- PMCID: PMC1274348
- DOI: 10.1086/324068
Niemann-Pick disease type C: spectrum of HE1 mutations and genotype/phenotype correlations in the NPC2 group
Abstract
In Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC), a genetic heterogeneity with two complementation groups--NPC1, comprising > or =95% of the families, and NPC2--has been demonstrated. Mutations in the NPC1 gene have now been well characterized. HE1 was recently identified as the gene underlying the very rare NPC2. Here we report the first comprehensive study of eight unrelated families with NPC2, originating from France, Algeria, Italy, Germany, the Czech Republic, and Turkey. These cases represent essentially all patients with NPC2 who have been reported in the literature, as well as those known to us. All 16 mutant alleles were identified, but only five different mutations, all with a severe impact on the protein, were found; these five mutations were as follows: two nonsense mutations (E20X and E118X), a 1-bp deletion (27delG), a splice mutation (IVS2+5G-->A), and a missense mutation (S67P) resulting in reduced amounts of abnormal HE1 protein. E20X, with an overall allele frequency of 56%, was established as the common mutant allele. Prenatal diagnosis was achieved by mutation analysis of an uncultured chorionic-villus sample. All mutations except 27delG were observed in a homozygous state, allowing genotype/phenotype correlations. In seven families (with E20X, E118X, S67P, and E20X/27delG mutations), patients suffered a severe and rapid disease course, with age at death being 6 mo-4 years. A remarkable feature was the pronounced lung involvement, leading, in six patients, to early death caused by respiratory failure. Two patients also developed a severe neurological disease with onset during infancy. Conversely, the splice mutation corresponded to a very different clinical presentation, with juvenile onset of neurological symptoms and prolonged survival. This mutation generated multiple transcripts, including a minute proportion of normally spliced RNA, which may explain the milder phenotype.
Figures

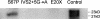
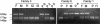
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for complete genomic DNA sequence of human HE1 [accession number AC005479] and HE1/NPC2 [accession number Q15668])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for NPC [MIM 257220 and MIM 601015])
References
-
- Baker CS, Magargee SF, Hammerstedt RH (1993) Cholesterol transfer proteins from ram cauda epidydimal and seminal plasma. Biol Reprod Suppl 48:86
-
- Blanchette-Mackie EJ (2000) Intracellular cholesterol trafficking: role of the NPC1 protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1486:171–183 - PubMed
-
- Carstea ED, Morris JA, Coleman KG, Loftus SK, Zhang D, Cummings C, Gu J, et al (1997) Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science 277:228–231 - PubMed
-
- Chiba-Falek O, Kerem E, Shoshani T, Aviram M, Augarten A, Bentur L, Tal A, Tullis E, Rahat A, Kerem B (1998) The molecular basis of disease variability among cystic fibrosis patients carrying the 3849+10 kb C→T mutation. Genomics 53:276–283 - PubMed
-
- Christomanou H, Vanier MT, Santambrogio P, Arosio P, Kleijer WJ, Harzer K (2000) Deficient ferritin immunoreactivity in tissues from Niemann-Pick type C patients: extension of findings to fetal tissues, H and L ferritin isoforms, but also one case of the rare Niemann-Pick C2 complementation group. Mol Genet Metab 70:196–202 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

