Syndromic short stature in patients with a germline mutation in the LIM homeobox LHX4
- PMID: 11567216
- PMCID: PMC1274372
- DOI: 10.1086/323764
Syndromic short stature in patients with a germline mutation in the LIM homeobox LHX4
Abstract
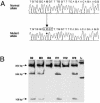
Studies of genetically engineered flies and mice have revealed the role that orthologs of the human LIM homeobox LHX4 have in the control of motor-neuron-identity assignment and in pituitary development. Remarkably, these mouse strains, which bear a targeted modification of Lhx4 in the heterozygous state, are asymptomatic, whereas homozygous animals die shortly after birth. Nevertheless, we have isolated the human LHX4 gene, as well as the corresponding cDNA sequence, to test whether it could be involved in developmental defects of the human pituitary region. LHX4, which encodes a protein 99% identical to its murine counterpart, consists of six coding exons and spans >45 kb of the q25 region of chromosome 1. We report a family with an LHX4 germline splice-site mutation that results in a disease phenotype characterized by short stature and by pituitary and hindbrain (i.e., cerebellar) defects in combination with abnormalities of the sella turcica of the central skull base. This intronic mutation, which segregates in a dominant and fully penetrant manner over three generations, abolishes normal LHX4 splicing and activates two exonic cryptic splice sites, thereby predicting two different proteins deleted in their homeodomain sequence. These findings, which elucidate the molecular basis of a complex Mendelian disorder, reveal the fundamental pleiotropic role played by a single factor that tightly coordinates brain development and skull shaping during head morphogenesis.
Figures



References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Burglin, T. R., http://www.biosci.ki.se/groups/tbu/homeo/consensus.gif (for information relevant to homeobox proteins and their classification and evolution)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for mouse Lhx4 cDNA sequence [accession number AF135415] and for human LHX4 cDNA sequence [accession number AF282899])
-
- GeneMap'99, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genemap99/ (for in silico mapping of human ESTs)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for Chiari type I malformation [MIM 118420] and Lhx4 [MIM 602146])
References
-
- Couly G, Le Douarin NM (1988) The fate map of the cephalic neural primordium at the presomitic to the 3-somite stage in the avian embryo. Development 103:101–113 - PubMed
-
- Dattani MT, Martinez-Barbera JP, Thomas PQ, Brickman JM, Gupta R, Martensson IL, Toresson H, Fox M, Wales JK, Hindmarsh PC, Krauss S, Beddington RS, Robinson IC (1998) Mutations in the homeobox gene HESX1/Hesx1 associated with septo-optic dysplasia in human and mouse. Nat Genet 19:125–133 - PubMed
-
- Dubois PM, El Amraoui A, Héritier AG (1997) Development and differentiation of pituitary cells. Microsc Res Tech 39:98–113 - PubMed
-
- Eagleson GW, Harris WA (1990) Mapping of the presumptive brain regions in the neural plate of Xenopus laevis. J Neurobiol 21:427–440 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

