The effect of EGTA and Ca++ in regulation of the brain Na/K-ATPase by noradrenaline
- PMID: 11570982
- PMCID: PMC56634
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-2-8
The effect of EGTA and Ca++ in regulation of the brain Na/K-ATPase by noradrenaline
Abstract
Background: The Na/K-ATPase activity of the brain synaptic plasma membranes (SPM) is regulated by noradrenaline (NA) and the synaptosomal factor SF (soluble protein obtained from the synaptosome cytosol). In the absence of SF, NA inhibits Na/K-ATPase, while, on addition of SF to the reaction medium, there is a NA-dependent activation of Na/K-ATPase. On the other hand, EGTA augments the Na/K-ATPase activity and attenuates the ability of NA to inhibit Na/K-ATPase.
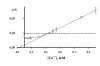
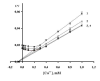
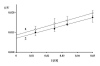
Results: Considering that Ca2+ ion is a Na/K-ATPase modifier, it can be assumed that the effect of NA and SF is a Ca2+-dependent process. However, in the presence of 0.3 mM EGTA and 0.1 mM NA, the apparent inhibition constant for Ca2+ (at [Ca2+] > 0.3 mM) is not SF dependent, while the apparent activation constant for SF does not change at increasing Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+] < 0.3 mM). At various Ca2+ concentrations (0.06, 0.35 and 0.6 mM), no significant changes occur in the mode of action of NA on the Na/K-ATPase activity in the presence of 5 microg/ml SF. EGTA also has no effect on the NA-independent activation of Na/K-ATPase evoked by high SF concentrations.
Conclusions: Taking into account that in the absence of EGTA similar results have been obtained, it can be concluded that the effect of NA and SF on brain Na/K-ATPase is a Ca2+-independent process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of noradrenaline-induced stimulation of Na-K ATPase activity in the rat brain: implications on REM sleep deprivation-induced increase in brain excitability.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Mar;336(1-2):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0260-9. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19823772 Review.
-
Norepinephrine induced alpha-adrenoceptor mediated increase in rat brain Na-K ATPase activity is dependent on calcium ion.Neurochem Int. 1999 Jun;34(6):499-507. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(99)00025-x. Neurochem Int. 1999. PMID: 10402225
-
The Na/K-ATPase regulation by neurotransmitters in ontogeny.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2000 Oct;108(4):360-70. doi: 10.1076/apab.108.4.360.4303. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11094387
-
The interaction between calcium and the activation of Na+, K+-ATPase by noradrenaline.Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 Mar;66(2):111-6. doi: 10.1007/BF00220778. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985. PMID: 2984541
-
In search of synaptosomal Na+,K(+)-ATPase regulators.Mol Neurobiol. 1992 Winter;6(4):359-75. doi: 10.1007/BF02757941. Mol Neurobiol. 1992. PMID: 1363048 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of noradrenaline-induced stimulation of Na-K ATPase activity in the rat brain: implications on REM sleep deprivation-induced increase in brain excitability.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Mar;336(1-2):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0260-9. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19823772 Review.
References
-
- Kometiani ZP, Tsakadze LG, Jariashvili TJ. Functional significance of the effects of neurotransmitters on the Na/K-ATPase system. Neurochemistry, 1984;42:1246–1250. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez de Lores Arnaiz G. In search of synaptosomal Na/K-ATPase regulators. Mol Neurobiol. 1992;6(4):359–375. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez de Lores Arnaiz G, Antonelli de Gomez de Lima M. Partial characterization of an endogenous factor which modulates the effect of catecholamines on synaptosomal Na,K-ATPase. Neurochem Res. 1986;11(7):933–947. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

