Murine gammaherpesvirus-68-induced interleukin-10 increases viral burden, but limits virus-induced splenomegaly and leukocytosis
- PMID: 11576228
- PMCID: PMC1783283
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01286.x
Murine gammaherpesvirus-68-induced interleukin-10 increases viral burden, but limits virus-induced splenomegaly and leukocytosis
Abstract
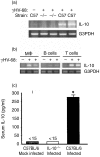
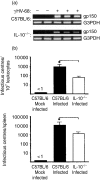
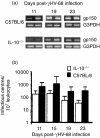
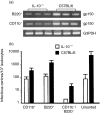
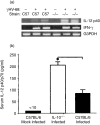
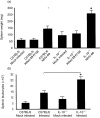
Based on its genomic sequence and its pathogenesis, murine gammaherpesvirus-68 (gammaHV-68) has been established as a tractable model for the study of viral infections caused by the human gammaherpesviruses, Epstein-Barr virus or human herpesvirus-8. Despite significant advances, the mechanisms responsible for gammaHV-68-induced alterations in the protective host response, and the accompanying virus-induced leukocytosis, are not clear. In the present study, we questioned whether viral infection resulted in endogenous interleukin-10 (IL-10) production that might alter the host response. Infection of C57BL/6 mice resulted in increased IL-10 expression, demonstrating that gammaHV-68 could induce endogenous production of this cytokine. Infected C57BL/6 mice demonstrated the characteristic splenomegaly associated with this viral infection, however, we were surprised to discover that the splenomegaly was greater in syngeneic mice genetically deficient in IL-10 (IL-10-/-). These results strongly suggested that endogenously produced IL-10 might serve to limit leukocytosis in wild-type mice. Quantification of viral burden demonstrated a significant elevation in C57BL/6 versus IL-10-/- mice, with increases in virus being observed in both the macrophage and B-lymphocyte populations. The decreased viral load in syngeneic IL-10-/- mice correlated with an increased expression of endogenous IL-12, suggesting a mechanism of protection that was IL-12 dependent. Taken together, these studies demonstrate a surprising dichotomy for endogenous IL-10 production during gammaHV-68 infection. While the lack of IL-10 results in increased IL-12 expression and a lower viral burden, IL-10-/- mice also experience an increased leukocytosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Murine gamma-herpesvirus-68-induced IL-12 contributes to the control of latent viral burden, but also contributes to viral-mediated leukocytosis.J Immunol. 2004 Jan 1;172(1):516-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.1.516. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14688362
-
Reduced CTL response and increased viral burden in substance P receptor-deficient mice infected with murine gamma-herpesvirus 68.J Immunol. 2003 Mar 1;170(5):2605-12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.5.2605. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12594288
-
Limited IL-6 production following infection with murine gammaherpesvirus 68.Arch Virol. 2006 Jul;151(7):1423-9. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0725-z. Epub 2006 Feb 20. Arch Virol. 2006. PMID: 16489506
-
Initiation of the host response against murine gammaherpesvirus infection in immunocompetent mice.Viral Immunol. 2004;17(4):473-80. doi: 10.1089/vim.2004.17.473. Viral Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15671745 Review.
-
Gamma interferon blocks gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency in a cell type-specific manner.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):6134-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00108-07. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17360749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Infection with murine gammaherpesvirus 68 exacerbates inflammatory bowel disease in IL-10-deficient mice.Inflamm Res. 2009 Dec;58(12):881-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-009-0059-x. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Inflamm Res. 2009. PMID: 19544045
-
Suppressive CD8+ T cells arise in the absence of CD4 help and compromise control of persistent virus.J Immunol. 2011 Jun 1;186(11):6218-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003812. Epub 2011 Apr 29. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21531895 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Gamma Herpesvirus MHV-68 Induces Severe Gastrointestinal (GI) Dilatation in Interferon Gamma Receptor-Deficient Mice (IFNγR-/-) That Is Blocked by Interleukin-10.Viruses. 2018 Sep 23;10(10):518. doi: 10.3390/v10100518. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30249047 Free PMC article.
-
The MHV68 M2 protein drives IL-10 dependent B cell proliferation and differentiation.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Apr 4;4(4):e1000039. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000039. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18389062 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of dendritic cells by a gamma2-herpesvirus induces functional modulation.J Immunol. 2005 Sep 1;175(5):3225-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.3225. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16116213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blaskovic D, Stanekova D, Rajcani J. Experimental pathogenesis of murine herpesvirus in newborn mice. Acta Virol. 1984;28:225. - PubMed
-
- Efstathiou S, Ho YM, Minson AC. Cloning and molecular characterization of the murine herpesvirus 68 genome. J Gen Virol. 1990;71:1355. - PubMed
-
- Efstathiou S, Ho YM, Hall S, Styles CJ, Scott SD, Gompels UA. Murine herpesvirus 68 is genetically related to the gammaherpesviruses Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus saimiri. J Gen Virol. 1990;71:1365. - PubMed
-
- Weck KE, Dal Canto AJ, Gould JD, O'Guin AK, Roth KA, Saffitz JE, Speck SH, Virgin HW. Murine gamma-herpesvirus 68 causes severe large-vessel arteritis in mice lacking interferon-gamma responsiveness: a new model for virus-induced vascular disease [see comments] Nat Med. 1997;3:1346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

