LAF1, a MYB transcription activator for phytochrome A signaling
- PMID: 11581165
- PMCID: PMC312796
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.915001
LAF1, a MYB transcription activator for phytochrome A signaling
Abstract
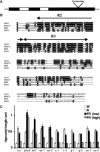
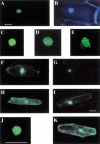
The photoreceptor phytochrome (phy) A has a well-defined role in regulating gene expression in response to specific light signals. Here, we describe a new Arabidopsis mutant, laf1 (long after far-red light 1) that has an elongated hypocotyl specifically under far-red light. Gene expression studies showed that laf1 has reduced responsiveness to continuous far-red light but retains wild-type responses to other light wavelengths. As far-red light is only perceived by phyA, our results suggest that LAF1 is specifically involved in phyA signal transduction. Further analyses revealed that laf1 is affected in a subset of phyA-dependent responses and the phenotype is more severe at low far-red fluence rates. LAF1 encodes a nuclear protein with strong homology with the R2R3-MYB family of DNA-binding proteins. Experiments using yeast cells identified a transactivation domain in the C-terminal portion of the protein. LAF1 is constitutively targeted to the nucleus by signals in its N-terminal portion, and the full-length protein accumulates in distinct nuclear speckles. This accumulation in speckles is abolished by a point mutation in a lysine residue (K258R), which might serve as a modification site by a small ubiquitin-like protein (SUMO).
Figures





References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Barnes SA, Quaggio RB, Whitelam GC, Chua NH. fhy1 defines a branch point in phytochrome A signal transduction pathways for gene expression. Plant J. 1996b;10:1155–1161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
