Central melanocortin receptors regulate insulin action
- PMID: 11581309
- PMCID: PMC200952
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12954
Central melanocortin receptors regulate insulin action
Abstract
Energy balance and insulin action are tightly coregulated. Leptin regulates energy intake and expenditure partly by modulation of the melanocortin pathway in the hypothalamus. Here we demonstrate potent effects of the melanocortin pathway on insulin action and body distribution of adiposity. Conscious rats received week-long infusions of either a melanocortin receptor agonist, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH), or antagonist, SHU9119, in the third cerebral ventricle while food intake was maintained constant in each group. alpha-MSH decreased intra-abdominal fat and markedly enhanced the actions of insulin on both glucose uptake and production, while SHU9119 exerted opposite effects. Our findings elucidate a neuroendocrine network that is likely to play a central role in the coupling of energy intake and insulin action.
Figures

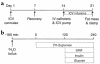
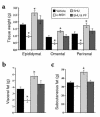
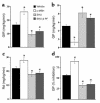

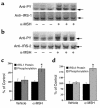
Comment in
-
Progress in the search for neuronal mechanisms coupling type 2 diabetes to obesity.J Clin Invest. 2001 Oct;108(7):963-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI14127. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11581296 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- McGarry JD. What if Minkowski had been ageusic? An alternative angle on diabetes. Science. 1992;258:766–770. - PubMed
-
- Petersen KF, et al. 13C/31P NMR studies on the mechanism of insulin resistance in obesity. Diabetes. 1998;47:381–386. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372:425–32. - PubMed
-
- Campfield L, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995;269:546–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

