Developmental alcohol and circadian clock function
- PMID: 11584552
- PMCID: PMC6707130
Developmental alcohol and circadian clock function
Abstract
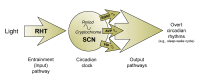
Studies in rats found that alcohol exposure during the early postnatal period, particularly during the brain-growth-spurt period, can result in cell loss in various brain regions and persistent behavioral impairments. Some investigators have speculated that the body's internal clock, which is located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) in the brain, may also be affected by developmental alcohol exposure. For example, alcohol-induced damage to the SCN cells and their function could result in disturbances of the circadian timekeeping function, and these disturbances might contribute to the behavioral impairments and affective disorders observed in people prenatally exposed to alcohol. Preliminary findings of studies conducted in rats suggest that developmental alcohol exposure may indeed interfere with circadian clock function as evidenced by a shortened circadian sleep-wake cycle and changes in the release of certain brain chemicals (i.e., neuropeptides) by SCN cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental alcohol exposure disrupts circadian regulation of BDNF in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2004 May-Jun;26(3):353-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2004.02.003. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2004. PMID: 15113597 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol consumption impairs the circadian rhythm of pro-opiomelanocortin and period genes mRNA expression in the hypothalamus of the male rat.J Neurochem. 2004 Mar;88(6):1547-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02300.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15009656
-
[Effects of ethanol on the development of circadian time keeping system].Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2007 Apr;42(2):67-75. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17508618 Review. Japanese.
-
Circadian regulation of sleep in mammals: role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005 Nov;49(3):429-54. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2005.01.005. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005. PMID: 16269313 Review.
-
[Understanding the action of the circadian clock: from phenomenologic ideas to molecular activity].C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1998;192(4):683-710. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1998. PMID: 9842472 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Long-term genomic and epigenomic dysregulation as a consequence of prenatal alcohol exposure: a model for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Front Genet. 2014 Jun 2;5:161. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00161. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24917881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental alcohol exposure is exhausting: Sleep and the enduring consequences of alcohol exposure during development.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024 Mar;158:105567. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105567. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024. PMID: 38309498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep problems among children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD)- an explorative study.Ital J Pediatr. 2021 May 17;47(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13052-021-01056-x. Ital J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34001186 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopmental alcohol exposure elicits long-term changes to gene expression that alter distinct molecular pathways dependent on timing of exposure.J Neurodev Disord. 2013 Mar 13;5(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1866-1955-5-6. J Neurodev Disord. 2013. PMID: 23497526 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effects of neonatal alcohol exposure on photic reentrainment and phase-shifting responses of the activity rhythm in adult rats.Alcohol. 2005 Oct;37(2):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2005.11.003. Alcohol. 2005. PMID: 16584971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonthius DJ, West JR. Alcohol-induced neuronal loss in developing rats: Increased brain damage with binge exposure. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1990;14:107–118. - PubMed
-
- Earnest DJ, Mahoney JC, Chen W-JA, Sohrabji F, West JR. Alcohol exposure during rapid brain development mimics the effects of aging on BDNF expression in the SCN and circadian timekeeping. Society of Neuroscience Abstracts. 1997;23:20.
-
- Goodlett CR, Kelly SJ, West JR. Early postnatal alcohol exposure that produces high blood alcohol levels impairs development of spatial navigation learning. Psychobiology. 1987;15:64–74.
-
- Hannigan JH, Martier SS, Chugani HT, Sokol RJ. Brain metabolism in children with fetal alcohol syndrome: A positron emission tomography study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1995;19(Suppl):53A.
-
- Ingram DK, London ED, Reynolds MA. Circadian rhythmicity and sleep: Effects of aging in laboratory animals. Neurobiology of Aging. 1982;3:287–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
