Physical and functional interactions of human DNA polymerase eta with PCNA
- PMID: 11585903
- PMCID: PMC99895
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7199-7206.2001
Physical and functional interactions of human DNA polymerase eta with PCNA
Abstract
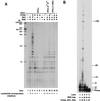
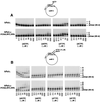
Human DNA polymerase eta (hPoleta) functions in the error-free replication of UV-damaged DNA, and mutations in hPoleta cause cancer-prone syndrome, the variant form of xeroderma pigmentosum. However, in spite of its key role in promoting replication through a variety of distorting DNA lesions, the manner by which hPoleta is targeted to the replication machinery stalled at a lesion site remains unknown. Here, we provide evidence for the physical interaction of hPoleta with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and show that mutations in the PCNA binding motif of hPoleta inactivate this interaction. PCNA, together with replication factor C and replication protein A, stimulates the DNA synthetic activity of hPoleta, and steady-state kinetic studies indicate that this stimulation accrues from an increase in the efficiency of nucleotide insertion resulting from a reduction in the apparent K(m) for the incoming nucleotide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interaction with PCNA is essential for yeast DNA polymerase eta function.Mol Cell. 2001 Aug;8(2):407-15. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00319-7. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11545742
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent coordination of the biological functions of human DNA polymerase iota.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48360-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406511200. Epub 2004 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15342632
-
Targeting of human DNA polymerase iota to the replication machinery via interaction with PCNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 4;98(25):14256-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261560798. Epub 2001 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11724965 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of ubiquitin in eukaryotic DNA translesion synthesis.Biochemistry. 2013 May 14;52(19):3217-28. doi: 10.1021/bi400194r. Epub 2013 May 1. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23634825 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of PCNA-dependent base excision repair.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;68:129-38. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(01)68095-4. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11554292 Review.
Cited by
-
FF483-484 motif of human Polη mediates its interaction with the POLD2 subunit of Polδ and contributes to DNA damage tolerance.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 27;43(4):2116-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv076. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25662213 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast DNA polymerase η possesses two PIP-like motifs that bind PCNA and Rad6-Rad18 with different specificities.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Nov;95:102968. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102968. Epub 2020 Sep 6. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32932109 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic switching for efficient and accurate translesion DNA replication.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Aug 27;32(15):4665-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh777. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15333698 Free PMC article.
-
Trf4 and Trf5 proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibit poly(A) RNA polymerase activity but no DNA polymerase activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;25(22):10183-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.22.10183-10189.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16260630 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of ubiquitin conjugation and SUMO modification of PCNA on replicational bypass of DNA lesions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 May;24(10):4267-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4267-4274.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15121847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailly V, Lauder S, Prakash S, Prakash L. Yeast DNA repair proteins Rad6 and Rad18 form a heterodimer that has ubiquitin conjugating, DNA binding, and ATP hydrolytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:23360–23365. - PubMed
-
- Bambara R A, Murante R S, Henricksen L A. Enzymes and reactions at the eukaryotic DNA replication fork. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:4647–4650. - PubMed
-
- Bloom L B, Chen X, Fygenson D K, Turner J, O'Donnell M, Goodman M F. Fidelity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme The effects of β, γ complex processivity proteins and ɛ proofreading exonuclease on nucleotide misincorporation efficiencies. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:27919–27930. - PubMed
-
- Brash D E. Sunlight and the onset of skin cancer. Trends Genet. 1997;13:410–414. - PubMed
-
- Cai J, Gibbs E, Uhlmann F, Phillips B, Yano N, O'Donnell M, Hurwitz J. A complex consisting of human replication factor C, p40, p37, and p36 subunits is a DNA-dependent ATPase and an intermediate in the assembly of the holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:18974–18981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
