Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 11585904
- PMCID: PMC99896
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7207-7217.2001
Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
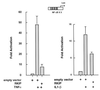
The Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) acts as a negative regulator of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (MAPK) cascade initiated by Raf-1. RKIP inhibits the phosphorylation of MAP/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) by Raf-1 by disrupting the interaction between these two kinases. We show here that RKIP also antagonizes the signal transduction pathways that mediate the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) in response to stimulation with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) or interleukin 1 beta. Modulation of RKIP expression levels affected NF-kappaB signaling independent of the MAPK pathway. Genetic epistasis analysis involving the ectopic expression of kinases acting in the NF-kappaB pathway indicated that RKIP acts upstream of the kinase complex that mediates the phosphorylation and inactivation of the inhibitor of NF-kappaB (IkappaB). In vitro kinase assays showed that RKIP antagonizes the activation of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) activity elicited by TNF-alpha. RKIP physically interacted with four kinases of the NF-kappaB activation pathway, NF-kappaB-inducing kinase, transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1, IKKalpha, and IKKbeta. This mode of action bears striking similarities to the interactions of RKIP with Raf-1 and MEK1 in the MAPK pathway. Emerging data from diverse organisms suggest that RKIP and RKIP-related proteins represent a new and evolutionarily highly conserved family of protein kinase regulators. Since the MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways have physiologically distinct roles, the function of RKIP may be, in part, to coordinate the regulation of these pathways.
Figures
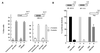
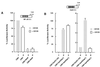

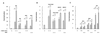


References
-
- Baldwin A S., Jr The NF-κ B and I κ B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- Banfield M J, Barker J J, Perry A C, Brady R L. Function from structure? The crystal structure of human phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein suggests a role in membrane signal transduction. Structure. 1998;6:1245–1254. - PubMed
-
- Banfield M J, Brady R L. The structure of Antirrhinum centroradialis protein (CEN) suggests a role as a kinase regulator. J Mol Biol. 2000;297:1159–1170. - PubMed
-
- Bradley D, Carpenter R, Copsey L, Vincent C, Rothstein S, Coen E. Control of inflorescence architecture in Antirrhinum. Nature. 1996;379:791–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
