Ectopic expression of DREF induces DNA synthesis, apoptosis, and unusual morphogenesis in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc: possible interaction with Polycomb and trithorax group proteins
- PMID: 11585906
- PMCID: PMC99898
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7231-7242.2001
Ectopic expression of DREF induces DNA synthesis, apoptosis, and unusual morphogenesis in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc: possible interaction with Polycomb and trithorax group proteins
Abstract
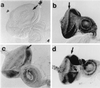
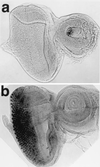
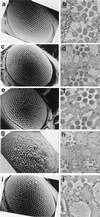
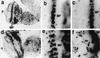
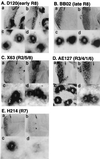
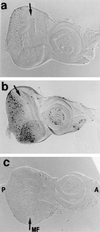
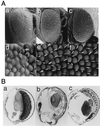
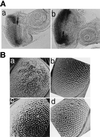
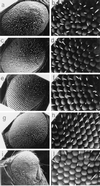
The promoters of Drosophila genes encoding DNA replication-related proteins contain transcription regulatory element DRE (5'-TATCGATA) in addition to E2F recognition sites. A specific DRE-binding factor, DREF, positively regulates DRE-containing genes. In addition, it has been reported that DREF can bind to a sequence in the hsp70 scs' chromatin boundary element that is also recognized by boundary element-associated factor, and thus DREF may participate in regulating insulator activity. To examine DREF function in vivo, we established transgenic flies in which ectopic expression of DREF was targeted to the eye imaginal discs. Adult flies expressing DREF exhibited a severe rough eye phenotype. Expression of DREF induced ectopic DNA synthesis in the cells behind the morphogenetic furrow, which are normally postmitotic, and abolished photoreceptor specifications of R1, R6, and R7. Furthermore, DREF expression caused apoptosis in the imaginal disc cells in the region where commitment to R1/R6 cells takes place, suggesting that failure of differentiation of R1/R6 photoreceptor cells might cause apoptosis. The DREF-induced rough eye phenotype was suppressed by a half-dose reduction of the E2F gene, one of the genes regulated by DREF, indicating that the DREF overexpression phenotype is useful to screen for modifiers of DREF activity. Among Polycomb/trithorax group genes, we found that a half-dose reduction of some of the trithorax group genes involved in determining chromatin structure or chromatin remodeling (brahma, moira, and osa) significantly suppressed and that reduction of Distal-less enhanced the DREF-induced rough eye phenotype. The results suggest a possibility that DREF activity might be regulated by protein complexes that play a role in modulating chromatin structure. Genetic crosses of transgenic flies expressing DREF to a collection of Drosophila deficiency stocks allowed us to identify several genomic regions, deletions of which caused enhancement or suppression of the DREF-induced rough eye phenotype. These deletions should be useful to identify novel targets of DREF and its positive or negative regulators.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ectopic expression of BEAF32A in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc inhibits differentiation of photoreceptor cells and induces apoptosis.Chromosoma. 2001 Sep;110(5):313-21. doi: 10.1007/s004120100155. Chromosoma. 2001. PMID: 11685531
-
Targeted expression of the DNA binding domain of DRE-binding factor, a Drosophila transcription factor, attenuates DNA replication of the salivary gland and eye imaginal disc.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Sep;19(9):6020-8. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.9.6020. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10454549 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expression of DREF in the Drosophila wing imaginal disc induces apoptosis and a notching wing phenotype.Genes Cells. 2001 Oct;6(10):877-86. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2001.00473.x. Genes Cells. 2001. PMID: 11683916
-
The DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory system: a master key for cell proliferation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Feb;1779(2):81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.11.011. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18155677 Review.
-
Stopped at the border: boundaries and insulators.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999 Apr;9(2):191-8. doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(99)80029-X. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999. PMID: 10322134 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of putzig Activity Results in Apoptosis during Wing Imaginal Development in Drosophila.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 20;10(4):e0124652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124652. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25894556 Free PMC article.
-
DREF is involved in the steroidogenesis via regulation of shadow gene.Am J Cancer Res. 2012;2(6):714-25. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Am J Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23226617 Free PMC article.
-
Redox regulation of DNA binding activity of DREF (DNA replication-related element binding factor) in Drosophila.Biochem J. 2004 Mar 15;378(Pt 3):833-8. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031601. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14651474 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila histone methyltransferase NSD is positively regulated by the DRE/DREF system.Genes Genomics. 2018 May;40(5):475-484. doi: 10.1007/s13258-018-0649-5. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Genes Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29892958
-
Drosophila Mi-2 negatively regulates dDREF by inhibiting its DNA-binding activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(14):5182-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.5182-5193.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12077345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asano M, Nevins J R, Wharton R P. Ectopic E2F expression induces S phase and apoptosis in Drosophila imaginal discs. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1422–1432. - PubMed
-
- Biggin M D, Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988;53:699–711. - PubMed
-
- Brizuela B J, Kennison J A. The Drosophila homeotic gene moira regulates expression of engrailed and HOM genes in imaginal tissues. Mech Dev. 1997;65:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Butler S J, Ray S, Hiromi Y. klingon, a novel member of the Drosophila immunoglobulin superfamily, is required for the development of the R7 photoreceptor neuron. Development. 1997;124:781–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
